Achievements
THE DYNAMIC CHANGE OF SOIL WATER AND ITS FACTOR ANALYSIS IN THE LOW PLAIN OF WESTERN JILIN PROVINCE
Liang Xiujuan1, Xiao Changlai1, Liang Xufeng2, Meng Xiaolu1 and Ma Zhe1
1 College of Environment and Resources,
2 College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang’an
Abstract: According to a lot of dynamic monitoring data of precipitation, soil water, groundwater and surface water, the temporal and spatial variation law of soil water (or soil moisture) content and its influencing factors in the western plain area of
Key words: soil water (or soil moisture) content, groundwater, temporal and spatial variation, influencing factors
1 Preface
By the influences of the climate and human activities, the water resources system has the vulnerability [1]. The great intensity of the human activities has changed many links of water cycle and affected the characteristics of the water resources system. That is to say, the human activities aggravate the vulnerability of the water resources system.
The distribution of the soil water in the nature is very complex, and the change of the soil water with the seasons depends on the contrast relation of the water balance factors in different years. If the recharge is more than the discharge, the soil water will increase; if not, it will decrease. Since the eastern area of
The condition of the soil water is controlled by the condition of the vapor, surface water and groundwater, as well as the atmospheric condition. The seepage of the precipitation or irrigation must pass the soil layer, so a part of the seepage is kept in the soil layer, which becomes the field capacity, and the redundant part recharges the unconfined water. The soil water is mainly consumed by the evaporation. If there is plant, the soil water can be absorbed by the plants [3].
The dynamic character of farmland soil water and its conversion is the central process of conversion among “four kinds of water” such as precipitation, surface water (including irrigation water), soil water and groundwater. It has the important meaning both in theory and practice for the continuous use of water-soil resources, and also in the agriculture production.
As the view of traditional development and usage of water resources, in contradictions of supplying and demanding for water resource, the ratio of water use for city living and industry is much more; correspondingly the ratio of water use quantity for agriculture, which forms the contradictions between cites and counties.
So it is important to research the temporal and spatial variation, influencing factors of soil water and its relationship with the groundwater for sustainable use of water resource and management.
2 Natural Geographical Situations
The researching area is located in the western field of
The area belongs to the
2.1 Characters of horizontal distribution
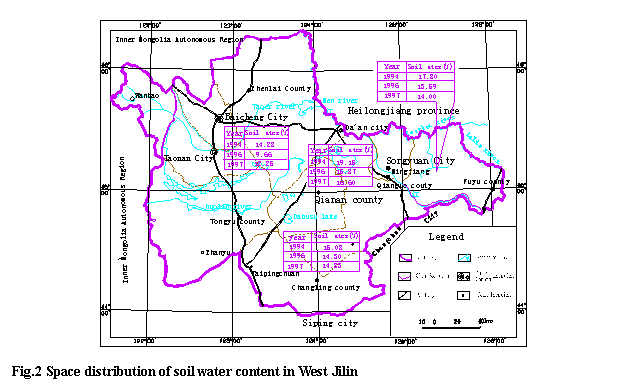
(1) The spatial distribution of soil water content in the area is different; it is highest in Qianguo; secondary is in Fuyu and Changling; and the lowest in Qian’an. There is definitive relationship between the character and its geographical conditions, in the area of Qianguo near the
(2) The soil water content is different with the target year; it is high in wet years ,low in dry years and it is between these two in a normal year, but the soil water content changes as the precipitation of the year.
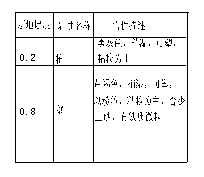
(3) The difference of soil water content in different years in different areas is different. The difference of wet year and normal year is much, but it is little between the normal year and dry year; In Qian’an, this difference between wet year and dry year is 4.63%; in Changling, the lowest soil water content is 0.78%, the values are 3.27% in Qian’an and 4.21% in Fuyu (Fig. 2). The result is that the surface soil of Qian’an is salty soil and sandy loam soil with poor retention, so the variation of soil water content is little; but the surface soil in Qianguo and Fuyu is mainly the sandy loam soil, the retention is between the two.
2.2 Character of vertical distribution
This can be classified as two kinds: Character of Vertical Distribution of soil water content in Qian’an and Changling is the same and that in Qian’guo and Fuyu the same.
(1) Qian’an to Changling
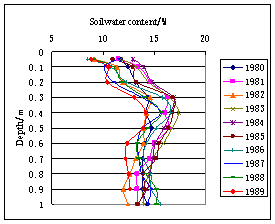
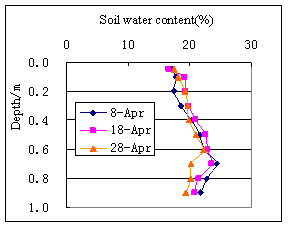
In the area of Qian’an and Changling, the soil water content in every layer of soil represents as : it is lowest in the soil of ground surface ,and increases downward gradually. To the depth of
|
|
Fig.3 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content (Changling) | Fig.4 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Changling) |
|
|
Fig.5 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Changling) | Fig.6 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Changling) |
(2) Qianguo and Fuyu
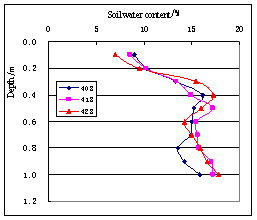
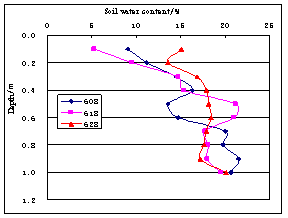
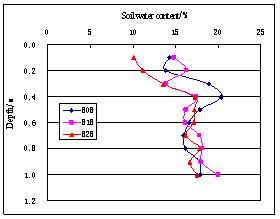
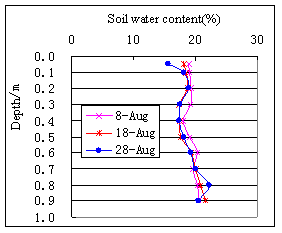
In the area of Qianguo and Fuyu, average soil water content is increasing with the depth in each layer of soil; it is increasing in the depth of
|
|
Fig.7 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Qianguo) | Fig.8 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Qianguo) |
|
|
Fig.9 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Qianguo) | Fig.10 Vertical distribution curve of soil water content(1994,Qianguo) |
3 Dynamic Characters of Soil Water Content
3.1 Annual dynamic changing characters
The characters of soil water content changing with time are basically the same in the researching area. From the beginning of Apple, soil water content increases ,and to the middle of May, it decreases gradually, in first July, it increases again, and to the October, it decreases again. At different depth , it's different in yearly amplitude. Surface soil water content is most variable, its difference could get to about 5%~12%; with the depth's increasing ,its changing is less, and bottom soil water has the lest change annual, its difference is about 3%~6%(Fig.11). Average soil water content of years is changing differently in yearly with the single layer, its difference is much in vertical value at the beginning of year, so the vertical distribution is obvious; but with the wet season's coming, difference of soil water content in vertically is less; soil water content in the surface and bottom soil is decreasing gradually (Fig 12).
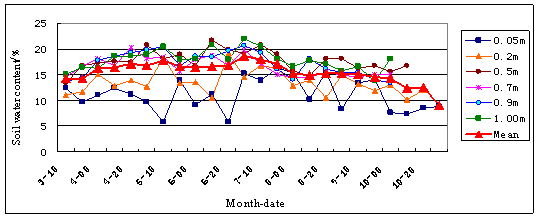
Fig.11 Annual dynamic curve of soil water content
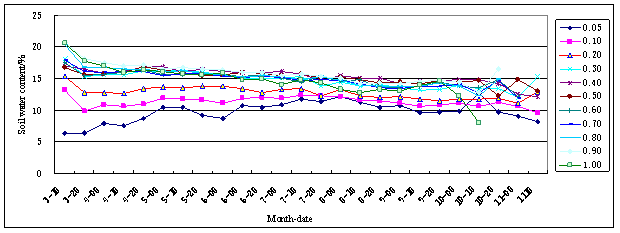
Fig.12 Multi-annual average dynamic curve of soil water content
3.2 Multi-annual dynamic changing characters
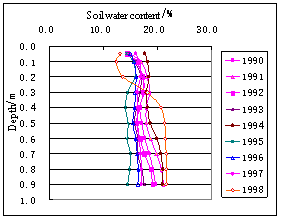
Soil water content has not only annual changes, but also the multi-annual changes, it’s changing surrounds some value with the time and in periodicity (Fig. 13).
The multi-annual changes of soil water content in the researching area are same in basically, annual average soil water content is changing with time; the variable characters are the same with precipitation and evaporation, and have the relationships with the precipitation of year.
The lowest value of each layer's soil water content in the dry year is much lower, and has the much changing in the year; but the lowest value of soil water content has the less changes in the wet year, and has the much changing in the year, too. The total variable tendency is as the same with the precipitation (Fig.14)
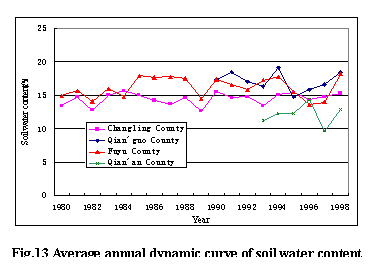
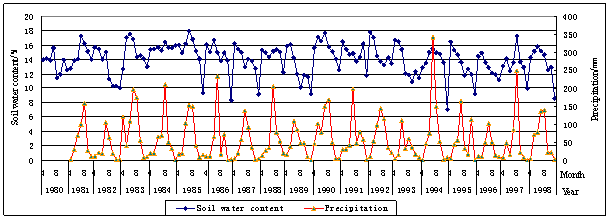
Fig.14 Multi-annual dynamic curve of soil water content
4 Analyzing the Influencing Factors to the Soil Water Content's Dynamic Variation
Impacts of contributing to the soil water content are many, ever complex. But they can be inducted to the aspects below:
4.1 Precipitation is the mean impact of variation of soil water content
Taking the graph of secular dynamic changing of soil water content for example, soil water content has the osculate relationship with precipitation; its value has the same changing tendency with precipitation basically, that is to say , soil water content is meanly effected by precipitation, but precipitation is higher than soil water content; precipitation is little, soil water content is less(Picture 15).
Except this, soil water content has relationships with precipitation, evaporation of last year and even quantity and intensity of precipitation of last time, and at the same time, such as surface runoff and conditions of runoff could impact on the value of soil water content.
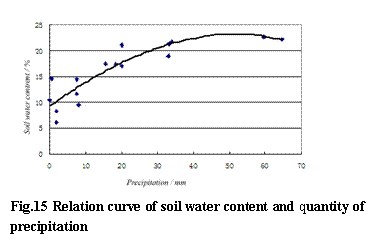
We studied the data of soil water content in last 20 years and the data of precipitation and runoff in last 50 years, in the situation of selecting or decreasing the other elements, dependent equation of soil water content and precipitation in
y = -2×10-5x3 - 0.0036x2 + 0.4972x + 9.2515
In the equation, R2 = 0.8075,correlation is good, that is to say, precipitation is the leading factor of changing of soil water content (Fig.15).
In the test of water penetration, which is taken in the mild clay, when seepage is stable, soil water content increases about 10%(weight), dry bulk density of soil is 1.4~1.5t/m3,and the value of soil water increasing is 14.0 ~15.0%(capacity), that is, in the condition of unsaturated, soil under the surface to the depth of
4.2 Rock character of formation is the control impact of soil water content
Value of soil water content and its distribution are effected by the rock character of formation, different thickness and component of plant soil, soil water content is different; the formation character under the plant soil is different, soil water content is different. The plant soil is thin in Qian’an, and the bottom formation is sandy soils, grains are big, permeability is well but retentiveness is bad, so the soil water content is low. The upper plant soil is thicker in Changling, about
4.3 Water level is influence factor of soil water content
In the generalized definition of groundwater, soil water is one part of groundwater; in the narrower definition of groundwater, soil water and groundwater are two different parts. Soil water content is a expression of soil water content. Soil water and groundwater are osculated. Precipitation gets to aquifer though the soil, in the process, if the initial soil water content is different, then the recharge into the groundwater is different, soil water content is high, it will get to the field capacity easily, the recharge that groundwater gets will be more; if the soil water content is low, the time which the soil gets to field capacity is long, it needs more recharge, so the recharge which groundwater gets will be less. In opposite, the water level is high, in the same climate condition, the evaporation is more, the recharge that soil gets from groundwater will be more, if the water level decreases, evaporation though the soil will be little, the recharge that soil gets from groundwater will be less, so the changes of water level has some affects to the soil water content.
The dynamic variation of soil water content is as the same of the dynamic of groundwater, but the dynamic variation of groundwater is later than the changing of soil water content. Though analyzing, we think that the delaying time that precipitation through the soil getting the groundwater is different with the season. In the spring, the weather is dry, and soil water content is less, delaying time is longer. In the summer, the weather is wet, soil water content is higher, and delaying time is shorter.
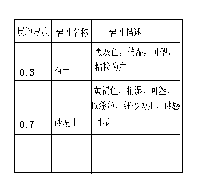
|
|
Fig.16 Stratigraphic column of Changling | Fig.17 Stratigraphic column of Fuyu |
5 Conclusion
The characters of temporal and spatial variation and the main influencing factors of soil water content are researched in western
Reference
[1] Liu Changming. Discussion on the Some Problems about China water Resources in 21st Century [J].Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2002,33 ( 1),15-19
[2] You Maozheng, Wang Huixiao. Soil water Resources Evaluation in Farm land.
[3] Zhang Weizhen, Shen Rongkai. Ground Water and Ground Water Regulation.
[4] Li Baoguo, Gong Yuanshi and Zuo Qiang, etc. Dynamic Model of Farmland Soil Water and its Application.