Evolutional Rules of Regional Groundwater System
FORMATION AND EVOLVEMENT OF GROUNDWATER SYSTEM OF TAIYUAN BASIN IN SHANXI
Hanying1,Yan Shi-long1 , CAO Jin-liang2,3 Wang gui-xi1,Ren jian-hui1, Zhang zhen-kui1
1 Shanxi Geology investigation institute,Taiyuan,030024;
2
3 Shanxi province
center of Geo-Environment Mornitoring,
Abstract: Taiyuan basin is the center of polity,
economy and culture of
Key
words:
Formation
and Evolvement of Groundwater System of Taiyuan
Basin in
1Formation and
evolvement of hydrogeologic structure of taiyuan
basin in
1.1 Basic tectonic framework of
1.1.1 Basic feature of Yanshan deformation structure
Yanshan deformation structure mainly
formed in Mesozoic Yanshan period (Upper Jurassic), which establishes the basic
tectonic framework of this basin. In Mesozoic, a formation sight alternating
anticlinorium and synclinorium appeared in Northwest-Southeast extrusion stress
field of Shanxi plot because Kula-Pacific Ocean
plate swooped down to Asia continent.
Meanwhile deformation structure had the characteristic of right-rotary cut.
Because of the effect of central Lishi–Yangquan West-East structure belt, there
was mainly Northeast anticlinorium in the North and there was mainly
north-north-east synclinorium. Primary zones of fracture were as follows, which
formed the boundary of groundwater system of
Xizhou mountain Northeast zone of fracture is developed in the north of Xizhou mountain. It tends towards N45ºE and its length is 100km. Because a series of approximately parallel inverted faultages are developed in this zone, terrane is vertical or inverted and terrane is slick between layers. This formation is the most developed at the bottom of Cambrian. The group piezotropy faultage was changed to normal faultage. Two sides of the faultage was slick between layers and it formed the separated water faultage.
Shilingguan-Kangjiahui latitudinal zone
of fracture is the first latitudinal formation zone. It is conjugate with
Xizhoushan faultage and longitudinal faultage in Shilingguan. There is
metamorphic rock in the north which dives to south and Cambrian-Ordovician
single tilted stratum in the south. Minitype folds and fractures are developed
in Cambrian shale and marlite nearby zone of fracture and they glide between
layers. So this faultage group forms the separated water boundary in the north
of
Liukefu-zhouhong mountain zone of
fracture is one part of southeast zone of fracture of Jingle syncline. Steep
stratum and mutual incised faultage makes the terrane in the whole lower
Palaeozoic outcrop between 1 and 3km.
This is normal faultage gliding between layers. Terrane on the zone of fracture
breaks up and it is attenuated. So this faultage group is considered the
separated water boundary in the northwest of
Shentanggou-Xishe longitudinal zone of
fracture in the north of Tunlan river forms the separated water boundary in the
west of
Shijiaping-Zhangjia river northeast
zone of fracture is located at southeast of Xiyan basin in the southeast of
Shanglancun-Donglingjing latitudinal zone of fracture intermittently emerges nearby north latitude 38 degrees, which is the second latitudinal faultage in this area. The east is developed in the zone of Huangling-Pingtou and the middle passes through the north of the Dongshan. The east-west positive faultage is developed in the zone of Houcun coal measures and the distance of some faultages reaches 350 meters.
There are three latitudinal zones of fracture near Guanjiayu in the south of Dongshan. Its structural feature is mainly closed parallel piezotropy normal faultage and interphase fold in the east-west direction and it has a tiled gradient descent in the south, which makes the depth of burial of Majiagou limestone descending to the direction of Yuci. The latitudinal structure extends to Shouyang and Niangziguan in the east, which is the permeable passage for karst water’s run-off to the deep of Niangziguan spring.
Pudong is from east-northeast fold
strap and extends to the northwest of Qinshui and the east of
1.1.2 Basic feature of himalayas period deformation structure
The fringe shovel fracture in the fault basin is concomitant with Mesozoic overturned faultage so that it cuts parts of overturned body, such as Xizhou mountain fracture. Another one is tensile shear faultage. It is along the former Mesozoic piezotropy fracture and forms tensility in Cenozoic, such as Qingxu-Jiaocheng fracture.
Taiyuan fault basin is one of Cenozoic fault zone in
Wanjin period controlling fractures in
North-northeast, east-northeast and
north-northwest fractures in fault basin are very developed and become tectonic
setting of
1.2 Geologic time
of formation of
Lithosphere
of the area rose before middle Jurassic and the whole suffered denudation.
Vertical reverse wring of Yanshan movement and vertical extrusion stress became
fiercely activated at the end of Jurassic, so that the platform of
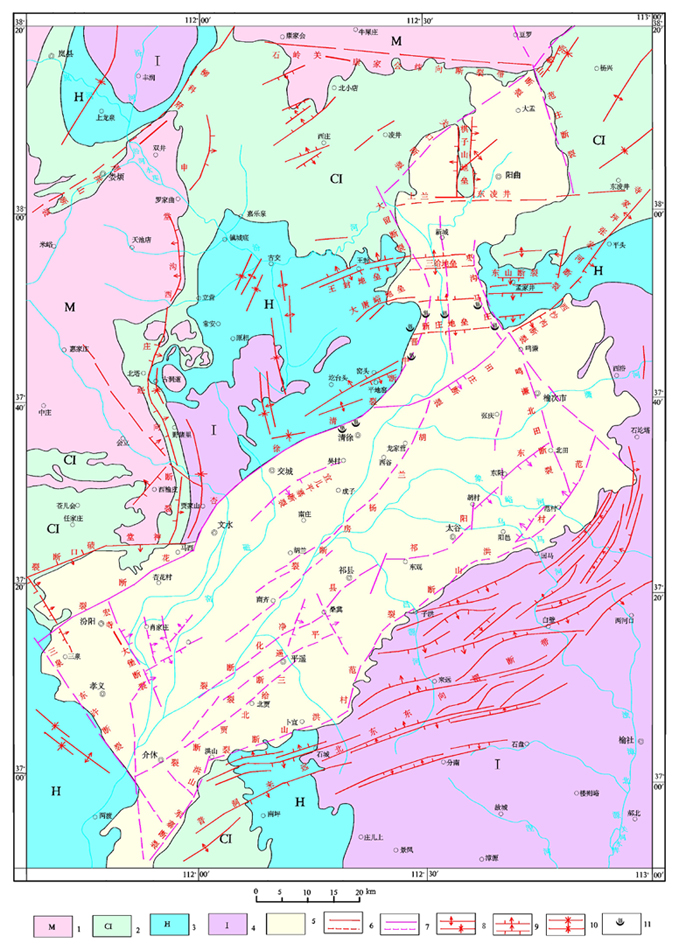
Figure1 structure outline map of fault basin in and
around
1.Precambrian System ⒉ Cambrian System, Ordovician system 3.Carboniferous System, Permian System 4.Triassic System,
Jurassic system 5.Cenozoic Erathem 6.Yanshanian structure 7.Himalayan structure 8.dorsally syncline 9.normal fault,reversed
fault 10. measured and conjectured structure 11.hot-water spot
denudation stage, so the stratum from Lower
Jurassic to Lower Tertiary was absent and Middle Jurassic suffered
denudation.At the end of Lower Tertiary, Himalayas
movement became fiercely activated and regional stress field changed reversely
from Yanshan reverse wring to normal wring. Under the control of new stress
field, the original northeast, north-northeast and east-northeast fracture was
traced and translated into tensile fracture. At the early of Upper Tertiary
north-south normal wring was suddenly enhanced so that superpower
northwest-southeast tensile stress was induced. The northeast, north-northeast
and east-northeast fracture was further tensed and some faultage sank along the
fracture. From then on upper Cenozoic started aggrading and
Fault subsidence mainly goes through two stages which are Pliocene overstep and Quaternary Period drape during its own development process. Fault subsidence continuously sank under tensile stress in Pliocene. Wangwuzu and Chengzizu were filled sediment on the early sediment stage. At that time the range of water area was small and the deeper concave accepted coarser red sediment which was mainly river phase. Wangwuzu had the character of conglomerate.
Hucunzu sediment accepted almost coarser red
sediment which was mainly river phase because the water area extended.The
middle period Pliocene which was from Xiguzu to Shijiashezu sediment stage was
lake basin heyday and Taiyaun fault sank steadily in this period. At that time
the lake was widely distributing. Not only Taiyuan fault became a major
lakeland ,but also a series of upper Cenozoic fault basin on Shanxi platform
which was from north Sangganhe fault to south Weihe fault all went through
lakebuilding stages. There was laky basin in Getaiyueshan of Yushe, Wuxiang,
Qinxian and Tunliu.At that time the biology was thriving because of moist
climate of
2. The evolution
of hydrodynamical field of quaternary groundwater system in
As far as the Quaternary pore water in Taiyuan basin is concerned,
its hydrodynamical field is mainly controlled by physical factor [1] in natual
state, pore-space phreatic water is recharged by atmospheric precipitation,
surface water and lateral runoff alongside of the basin and its main discharge
method is manual exploitation and Evaporation .and its main discharge method is
manual exploitation and Evaporation. Before the 1970s, confined water in middle
or deeper layer recharged the shallow phreatic water by virtue of upswing
leakage because the mining quantity of confined water was so small that
confined level is higher than phreatic water level. Since the 1970s, the mining
quantity of quaternary pore water in taiyuan basin has been on the increase; in
successive years, substantial overmining of ground water has lead to a
substantial descent of water level both in area and quantity while the range of
drawdown cone has been enlarging,which has resulted a radical change of
hydrodynamical field of quaternary groundwater system in the basin. Because of
the substantial overming of confined pore water in middle or deeper layer,
confined level has been 3-16m
widely lower than shallow pore water and confined pore water in middle or
deeper layer is recharged by shallow phreatic pore-space water by virtue of
downward leakage .confined pore-space water has become the main discharge
method of phreatic water in the basin.For
the groundwater system of Taiyuan basin, the
discharge quantity is larger than recharge quantity in a normal year, and the
water Level of ground water has been declined year by year and exploition and
utilization of groundwater by man has become a main discharge method of
quaternary pore water in
Pore water in loose rock distributes over loess undulating area of the basin, intermontane valley and plain which is the main area.
Containing-water System in the basin has a single tectonics, and grades into a multiple structure in the middle; therefor, ground water gradually grows to shallow phreatic pore-space water and confined pore water in middle or deeper layer from phreatic water .and the basin has gradually lowered toward the central section from the relatively higher sides of constituented by hills and dip plain, and thus formed an open and even landform. Ground water lies in the porous medium and it is characteristic of vertically alternating and horizontal translation.At the upper part of the Bianshan proluvial fan and dip plain, the water-bearing media is made up of sandy gravel and grit, which has a single hierarchy and a great thickness .The ground water has a great depth of burial as well as a great hydraulic gradient .The ground water gives priority to horizontal transmission and is primarily recharged by lateral runoff from bedrock while the vertical transmission is primarily recharged by vertical influent seepage from precipitation. At the lower part of the dip plain and the central section of the basin, the radient of the landform becomes small and the component of the water-bearing media gets fine. The aquifer grades into multiple structure from a single structure, whose monolayer thickness gets thin and whose hierarchies increase in number .The aquitard among the monolayer increases in number and thickness, and the depth of burial of groundwater level get shallow from deep, and the hydraulic gradient gets small from big, and runoff condition weakens .The changs of a series of hydrogeologic factors stated above result in the changes of the movement mode of the groundwater. The movement of groundwater gives priority to vertical alternating movement from horizontal movement .In the extensive and even alluvial plain, horizontal runoff of ground water is considerably feeble and the movement of groundwater gives priority to vertical alternating movement in shallow and middle layer because the hydraulic gradient is quite small.As far as aeration zone and fluctuation belt of water table in plain is concerned, the lithology gives priority to sand loam and grainsize is coarse and soil texture is loose and the depth of burial is shallow .The recharge by precipitation, irrigation and surface water translates into uninterrupted underground flow through the store adjustment of the shallow pore water system. Part of the precipitation infiltrate in the form of leakage crossing the aquitard and recharges the confined pore water in the middle layer below and another part of
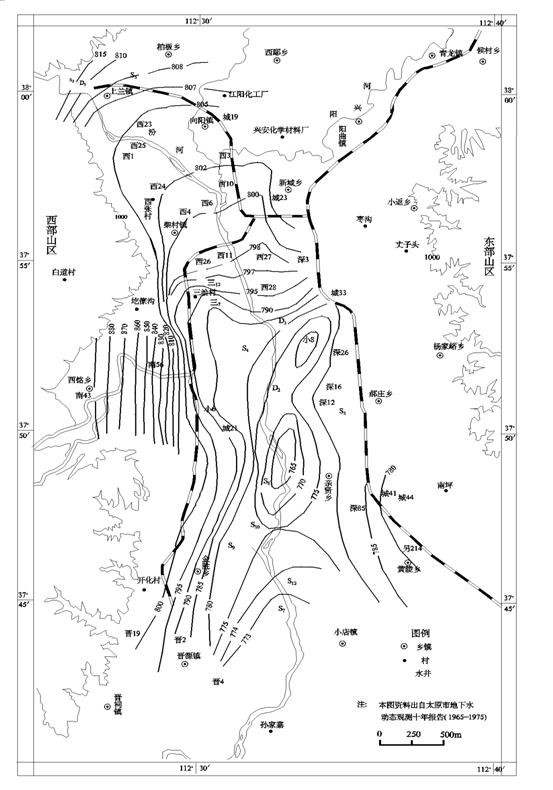
Figure2 measured underground flow
field of
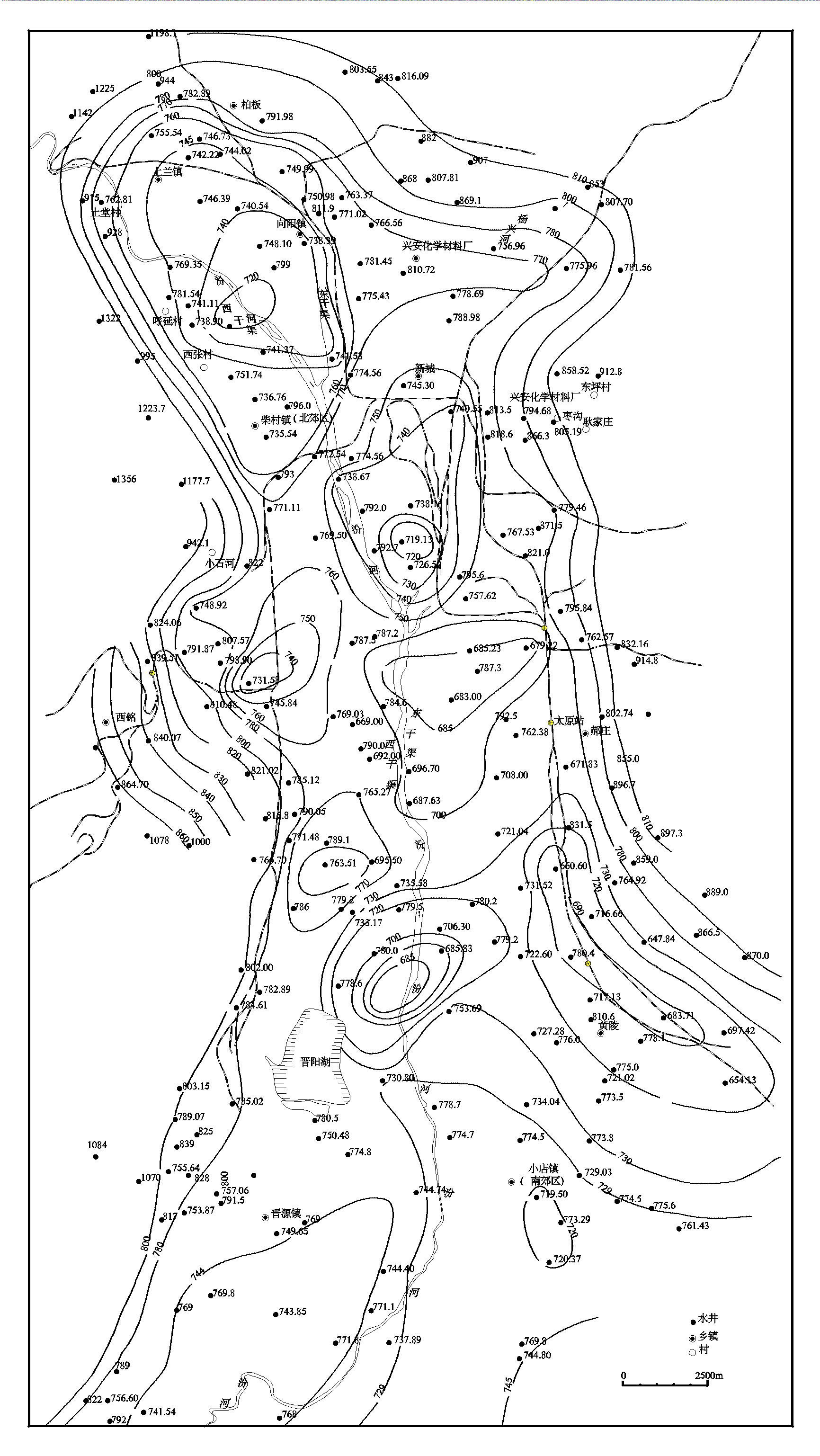
Figure3
measured underground flow field of
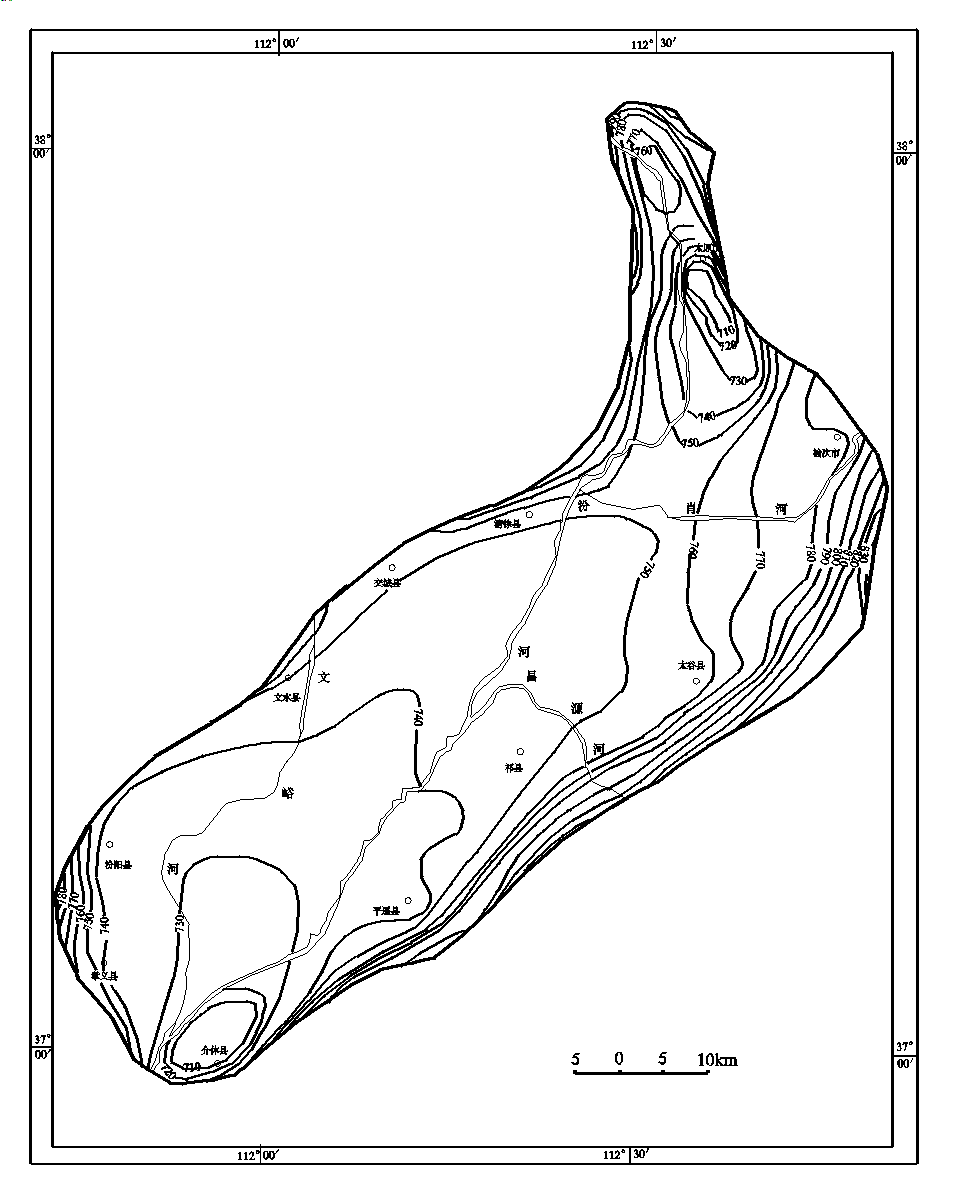
Figure4 measured underground flow
field of
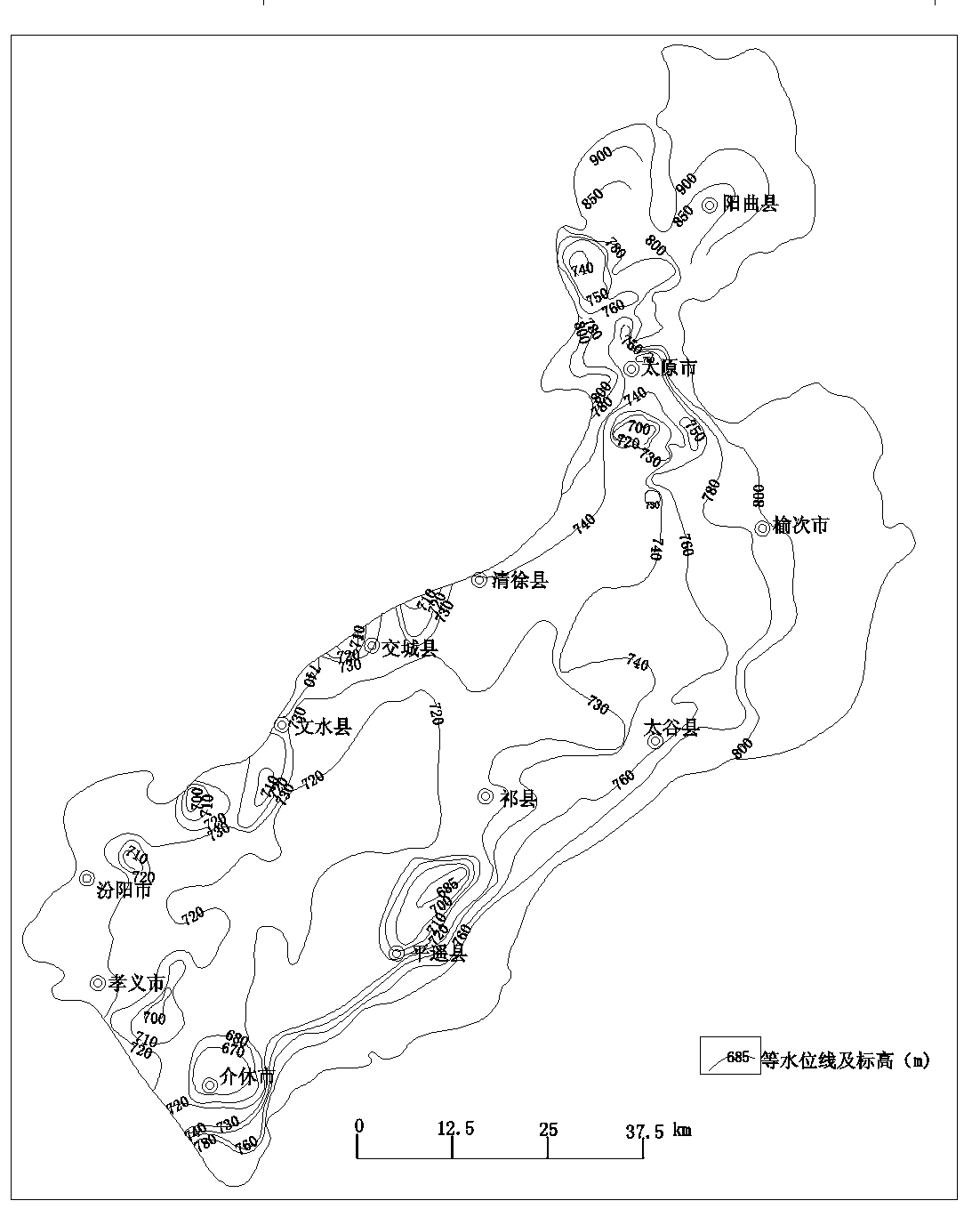
Fig 5 measured underground flow
field of
precipitation is consumed in evaporation. The fundamental movement mode of groundwater is vertical alternating movement of ground water.
2.1 Dynamic performance of shallow
pore water in
The
dynamic performance of shallow pore water in
2.1.1 Weather runoff -type
It
mostly appears in loess undulating area and upper part of dip plain and isn't
influenced directly by precipitation .And the source of replenishment is mainly
underground runoff from mountain area .Ground water lags behind recharge of
precipitation. The lowest water level appears during June to September each
year. After the flood season, water level rises slowly until the highest water
level appears in January_ March next year. Water level begins to fall slowly in
March .The dynamical drift of shallow pore water in this area essentially keeps
natural state.See the dynamic performance graph
of shallow seated groundwater level at
2.1.2
exploitation-weather typeIt distributes
over the lower part of dip plain and zone of exploitation is the main zone of
exploitation of ground water, which has a shallow depth of burial on an average
of 4-20m .The source of
replenishment of groundwater is mostly underground runoff and precipitation
inleakage. Dynamic performance of Groundwater level is greatly affected by
exploitation. Secondly, water level is obviously affected by precipitation
because of a shallow depth of burial .during the exploitation, there occurs a
great drawdown in water level and the low water level generally appears in
June-July .with the arrival of flood season, the exploitation quantity
decreases and begins to rise due to precipitation and the highest water level
in a year appears in October and November. See the dynamic performance graph of
shallow seated groundwater level at
2.1.3 Exploitation-hydrology type
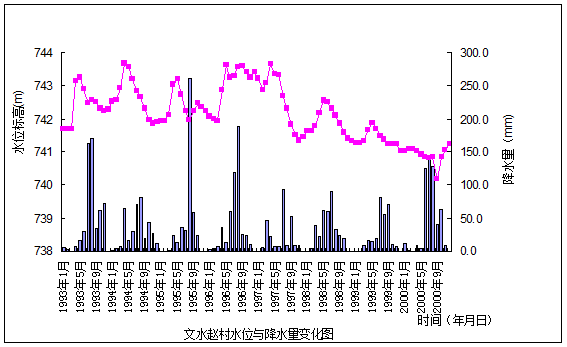
It Mostly distributes over irrigated area in alluvial plain .water depth of burial in Fenhe River alluvial plain is 2 to 10m, whose range of stage is great and often appears in indentation .the variation in water level is affected by surface water irrigation, precipitation inleakage and groundwater mining etc. Because of surface water inleakage caused by spring irrigation, groundwater level rise acutely and the highest water level usually appears in Aprial and May; afterwards ,the Ground water level falls rapidly and then begins to rise again because of precipitation inleakage recharge or ceasing exploitation .See dynamic performance graph of observational well at Zhao village ,Wenshui. The range of water level in a year is 2 to 3m and the range of water level between years is 2 to 5m. 2.1.4 Exploitation-runoff type
It mostly distributes over zone of hopper caused by drawdown in deep layer. The exploitation of water head site resulted in recession of level in deep underground water and caused a widened hydraulic gradient and thus shallow seated groundwater recharged the deep zone water through leaking recharge and the shallow seated groundwater level gradually decreased ,for example, the shallow seated groundwater in Xizhang and Beiying etc gradually run dry and got Discarded.
2.2 Dynamic performance of pore water in deep zone of taiyuan basin
Deep zone pore water level is restricted by lateral runoff, leaking recharge of shallow seated
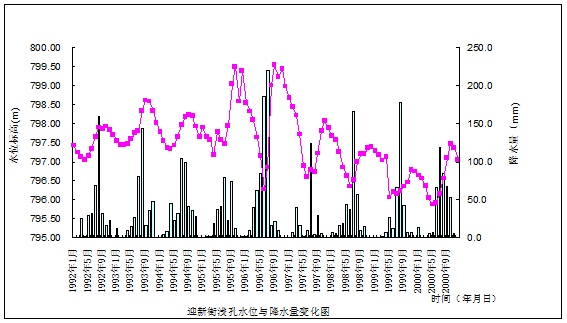
groundwater and manual exploitation .the water level presents a downtrend because of a great quantity of exploitation of deep zone pore water. The dynamic performance type may be divided into three sub-types exploitation drop type, runoff -exploitation type and
weather runoff type.
2.2.1 Exploitation-drop type.
This type Distributes over most of alluvial plain and the lower part of dip plain.the water level is mainly dominated by exploitation quantity and physical factor has a feeble effect on Groundwater level .groundwater mining has been increasing rapidly since April and dropped and the water level dropped to lowest point .afterwards precipitation grows in number and exploitation Quantity decreases and thus water level rises again. See the dynamic performance graph of exploitation- drop type in deep zone at Xiaodian.
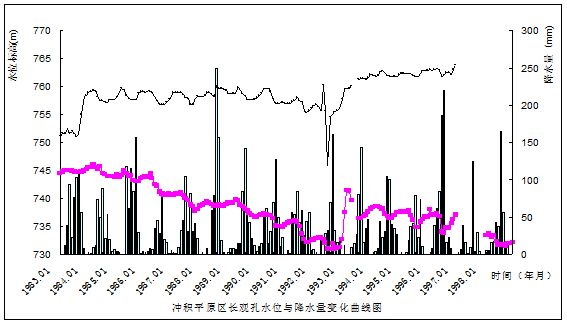
2.2.2 Runoff- exploitation type
It distributes over the upper part of alluvial-proluvial fan and spacious Dip plain, which is the main exploitation zone of ground water. Groundwater regime is affected by runoff and exploitation and Groundwater level totally presents a downtrend .during the exploitation, there is a great decreasing amplitude in water level and dynamical drift curve of water level over the years presents a funnel form .Lowest water level in a year appears in March –June. Generally water level begins to rise lagged behind the rain season about one month, which reflects that groundwater movement gives priority to horizontal runoff and that range of water level in a year is 3 to 20m and that range of water level over the years is great. See the dynamic performance graph at Wenshui Kaishan.
2.2.3 Weather-runoff type
It mostly
distributes over hilly ground and
lesser and range of water level in a year is small and smooth. It is a dull season of water utilization during January to March, and underground runoff underground runoff and recharge are intense while the
variation in water level is smooth .exploitation quantity gradually increases from April and thus water level has a slight drawdown .water level rises again after July because precipitation increases and exploitation quantity decreases.
2.3 Dynamic comparison between shallow layer and middle or deeper layer pore water
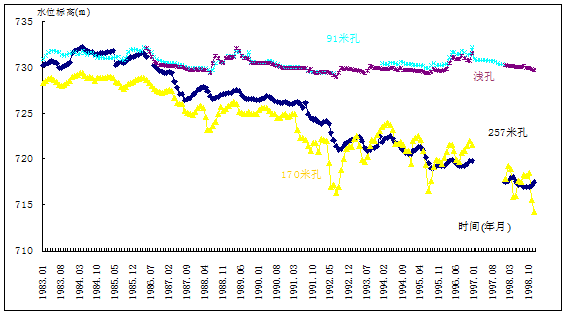
Compare the dynamical drift curve of pore water over the years in shallow layer and middle or deeper layer and it is observed that the curve of shallow layer is relatively steady while the curve of middle or deeper layer has an obvious downtrend. See the dynamic performance graph over the years at Changguankong, Xiaoyi in the basin.
2.4 Forming and
evolution of ground water drawdown cone in
In recent years ,on
the one hand there is a reductive tendency in precipitation in
The dynamic performance graph over the years at Changguankong,Xiaoyi county
recharge and recovering, and thereby local ground
water level continually drop down and extensive
drawdown cones come
into being in urban area and
The deep water zone of hopper in Taiyuan was earliest found in 1965, which centers in Caiyuan water factory and the depth of burial is 16.15 m and water level elevation is 767.0m.closed area of 770m water table contour is about 11.2 km2.At the same time, there is a local drawdown cone in Beiying with an area of about 5 km2.
In 1972, the closed area of 770m water table contour is up to 74 km2 and depth of burial at the center is 33m and water level elevation is 750m .the area of hopper zone extends to 17 km2. The depth of burial at the center is 23 m and water level elevation is 755 m.
In 1976, the hopper at Beiying joined with the urban hopper centered in the zoo and Caiyuan water factory. The center of urban hopper transfers southwester because the exploitation degree exploitation degree of Xiaowang village water factory and chemical water factory was increasing. The depth of burial at the center is 46.0 m and water level elevation is 737.80 m.
The depth and area of hopper zone rapidly increased in 1981.The drawdown at the Zoo water factory is largest and depth of burial is 67 m and water level elevation is 716 m. The 770 m water table contour is 25- km long in north and south, 11 km wide in east and west and the closed area is 275 km2.
In 1984, the hopper form was relatively steady except that the northern area, and the depth of burial at the center was 71m and the water level elevation was 712m. After 1980 the speed of descent at Beiying hopper sped up and the burial depth of highest hydrostatic level was beyond 90m and the water level elevation was 707.86m. And annual rate of descent was 4.7m. rate of descent of Wusu hopper was as intense as that of Beiying since it was found in 1981 .the depth of burial at the center of Wusu hopper 65.6 m and 128.34m in 2001 with a water level elevation of 654.06m; compared with that of 1984, the rate of descent in 17 years was 3.69 m; depth of burial in 2003 was 128.27 m and water level elevation was 654.13 m.
In 1982, the deep water drawdown cone in Xizhang zone firstly appeared Beigunian village in 1982 and then appeared in Xizhang village. The Lowest water level elevation was 776.91 m and the closed area of 780m water table contour was 15 km2 in 1982 and extended to 48.2 km2 in 1984 with a water level elevation of 768.74 m at the center.
Depth of burial at the center of Xizhang hopper was 44.4m in 1990 and water level elevation was 754.76m, and the closed area of water table contour was 57.21km2. The hopper in the urban area was 29.2 km long in south and north and 15.5 km wide in east and west; the closed area of 740 m water table contour was 248 km2, including 3 dropdown center all together, of which the biggest dropdown center was in urban area with a lowest depth of burial at center of 87.65 m and a water level elevation of 695.24 m. The depth of burial at the center of Xizhang in 1996 was 65m with an open bottom and the closed area of 770 m water table contour was 72 km2. The variation of the hopper in urban area was bigger. The range of the Hopper shrunk ,while the single depth increased ;the Hopper was 25km long in south and north and was 12km wide ;the closed area of 740m water table contour was 213km2 including 3dropdown center of which the depth of burial of Dama-Qinxian Hopper was deepest (101.4m deep with an elevation of 683.64m).
Because
the drawdown cone in Xizhang was restricted by Geographic conditions ,In 2000 ,
the closed area of 760m
water table contour dropped to 60 km2
and depth of burial at the center dropped down to 52.80 and water level
elevation dropped down to 749.70- 742.49
m and the 770 m
water table contour was linked together with the urban area. The Hopper in Urban
area joined with the Hopper in Beiying and thus a tremendous Hopper zone
covered the whole urban area of
In 2003, the depth of burial of the centre of drawdown cone in Xizhang was 63.66 m, and water level elevation was 743.03 m and the closed area of 760mwater table contour was 55 km2. The variation of the hopper in urban area was bigger. The 740 m water table contours joined together in the basin including 3 dropdown centers.(see 2003 water level contour map). The depth of burial of dropdown center in Beiying was 175.06 m and water level elevation was 627.94 m, and the closed area of 700m water table contour was 14 km2. The depth of burial of dropdown center in Wujiabu was 98.45 m and water level elevation was 676.55 m, and the closed area of 730 m water table contour was 55 km2. The depth of burial of dropdown center in Wujiabu was 98.45 m and water level elevation was 676.55 m, and the closed area of 730 m water table contour was 55 km2.
The center of drawdown cone in middle or deeper layer in Jiexiu lay around Songgu,Jiexiu. In 1977, the depth of burial of center of Hopper was 41 m and the closed area of 71 m water table contour was 103 km2. In 1984, the depth of burial of center of Hopper was 50.47m which was 9.47 m lower than that in 1977 with an Average rate of 1.35 m and the closed area of 720 m water table contour extended to 130 km2. In 2003, the depth of burial of Hopper was 66.22m and the total descent was 64.21m, and the Average rate of descent over the years was 1.78m and the closed area of 720m water table contour was 287km2.
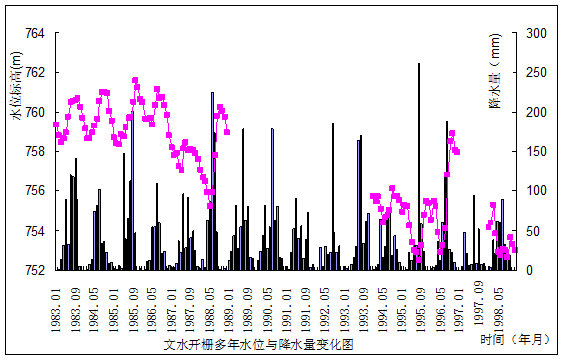
The depth of burial of drawdown cone in Bianshan, Wenshui was 64m in 1987 and became 170m in 2003 with a drawdown of 106m, and the Average rate of descent over the years was 6.62m; and the closed area of 730m water table contour was about 104km2. The depth of burial of drawdown cone in Bianshan, Wenshui was 64m in 1987 and became 170m in 2003 There are two drawdown cone altogether in Fenyang: one lies in Xinghua town, Fenyang city and the other lies in Tian village, Fenyang city. The drawdown cone in Xinghua town was earliest Found in 1985 and the depth of burial was 18.15m then and became 112.61m in 2003, and the closed area of 730m water table contour was 18km2. The drawdown cone in Tian village lay in the west of Fenyang city and was earliest Found in 1987and the depth of burial was about 64m then and became 164.80m in 2003 with a drawdown of 100.8m, and the Average rate of descent over the years was 6.3m, and the closed area of 720m water table contour was 16km2.
Form 1 Statistical list
of drawdown hopper in middle or deeper layer in
|
漏斗名称 |
闭合等水线(m) |
中心水位(m) |
出现雏形年份 |
水位下降(m) |
下降速度(m/a) |
涌水面积(Km2) | |||
|
埋深 |
标高 | ||||||||
|
太原市 |
城区 |
740 |
128.4 |
678.60 |
1965 |
102.55 |
2.70 |
236 | |
|
西张 |
760 |
63.66 |
743.03 |
1969 |
61.67 |
1.87 |
55 | ||
|
晋中 |
介休 |
720 |
66.22 |
669.68 |
1967 |
64.21 |
1.78 |
130 | |
|
吕梁 |
交城边山 |
730 |
675 |
675.6 |
1987 |
49 |
3.06 |
41 | |
|
文水 |
730 |
170 |
668 |
1987 |
106 |
6.62 |
104 | ||
|
汾阳 |
田村 |
720 |
164.80 |
655.5 |
1987 |
100.8 |
6.3 |
16 | |
|
杏花镇 |
730 |
112.61 |
677.74 |
1985 |
94.46 |
5.24 |
18 | ||
Compare the two maps of flow field measured in August, 2003 and May, 1989 and it is observed that the variation of flow field of shallow pore water isn't great for the entire basin, on the one hand, it is related with the abandon of the shallow well and the reduction of exploitation quantity of shallow seated groundwater, on the other Hand ,it is related with the good adjusting capability and that of shallow seated groundwater is easy to recover. However, the variation of pore water flow field in middle or deeper layer was relatively great. In 1989,only obvious Hoppers appeared in Urban area of Taiyuan city ,Pingyao county, Jiexiu county etc; and groundwater drawdown Hoppers appeared at nearly all of nearly all of county seats such as Taiyuan , Bianshan Jiao cheng City, Wenshui, Fenyang , Xiaoyi, Jiexiu , Pingyao etc.The local water lowering and human activities caused a tremendous Change of Ground water hydrodynamic field. Among others, the recession of level of Hopper in the neighbourhood of Wenshui, Fenyang was up to 5 to 6m/a.
3.The Characteristic and Space Time Evolvement of Hydrochemistry Field in the Basin
3.1 Hydrochemistry characteristic of the basin
3.1.1 Hydrochemistry characteristic of shallow pore water
Shallow pore water in the middle and upper part of clinoplain in the north, east and southwest of the basin is strongly alternate. The degree of mineralization is smaller than 0.5g/l and the type of hydrochemistry is HCO3—Ca.Mg or HCO3—Ca.Na. The type of hydrochemistry is HCO3·SO4—Ca.Mg and the degree of mineralization is 0.5 to 1.0 g/l in the west and northeast of the basin and Bianshan because of the influence of coal stratum in Carboniferous.
The
type of shallow pore water of diluvial clinoplain is all HCO3·SO4 or SO4·HCO3,
except that the type of water is HCO3 in
partial area. The groundwater of this area directly accept side replenishment
of Bianshan groundwater and inleakage replenishment of precipitation. The
degree of mineralization is higher and it is 3165 mg/l because of finer
particle, shallower water table, slower velocity of flow and stronger
evaporation. The degree of mineralization is greater than 3 g/l and the type of hydrochemistry is S—M·C. For
example, the degree of mineralization is 5.26
g/l and total hardness is 3165 mg/l in Jinyuan,
Because the content of sulfate ion is generally higher in western area, the type of hydrochemistry in diluvial clinoplain is SO4·HCO3. The distance of flowthrough is short and the particle of unconsolidated sediment is big, so cation exchange adsorption is insufficient and cation is still Ca·Mg. The terrain of the east is very flat and the thickeness of unconsolidated sediment is very big. The type of hydrochemistry in the east is HCO3·SO4 and the type of hydrochemistry in partial area is HCO3 because of finer particle and stronger evaporation. Exchange adsorption of cation takes place in the soil and Na+ exchanges Ca2+ and Mg2+. The concentration of Na+ in the water heightens clearly and the type is HCO3—Na.Ca.
The type of hydrochemistry in alluvial plain is complicated because the buried depth of watertable is shallow and it is affected by human. The type is SO4·Cl or HCO3·Cl and the degree of mineralization is generally 3 to 5g/l. Water in alluvial plain of Taiyuan city is diluted by the water of Fenhe, so the water quality along the Fenhe is very good. The type in Lancun, Zhaozhuang and Xizhai is HCO3—Ca.Mg and the degree of mineralization is smaller than 1g/l. But the type in the else area is SO4·HCO3, SO4·Cl and HCO3·Cl.
The type of water in the middle of the basin is NaCl water and the degree of mineralization is 3 to 5 g/l,such as Xiaodian, Beige, Wangda, Nanbaijiazhuang, Ninggu and Yanwu. The ground water discharge in middle of the basin is mainly vertical evaporation and salinity is continuously enriched. Mobility of Cl is very strong, so HCO3 and SO42 in the groudwater becomes saturated and starts chemical precipitation. Meanwhile, domestic sewage discharge of basin occupant and wastewater irrigation to farmland creats mobility condition to Cl.
In the last tens years, with a great deal of groundwater exploitation in industry and agriculture, the groundwater table in basin descends year by year. The large area salted earth distributed in qingxu, jiaocheng, wenshui and fenyang is under control generally. The degree of mineralization, total hardness and the content of every ion descend.
The
TDS of Shallow pore water in the basin gets higher from north to south and from
mountainside to basin center. It is noticeable that TDS chorogram and
watertable buried depth figure of shallow pore water is analogical. For
example, minima watertable buried area (watertable buried depth<4m) which is located in xiaodianqu(
3.1.2 Hydrochemistry characteristic of pore water in semideep stratum
Water quality of pore water in semideep stratum is superior to shallow pore water. The hydrochemistry type of basin pore water accords with its hydrodynamic condition.The replenishment area of basin pore water is situated at the north, west and east of Bianshan. The fall of phreatic water surface in this area is big and the velocity of groundwater is quick, so its hydrochemistry type is mainly weight carbonic acid and weight carbonic-sulfuric acid. Runoff area is situated in the middle to south part of the basin and topograph is smooth and the fall of water table is small. The velocity of groundwater is very slow, so the hydrochemistry type is mainly weight carbonic acid-sulfuric acid-chloride whose degree of mineralization is higher. Discharge area is situated in the south of the basin.The hydrochemistry type turns into hypersalinity carbonic acid-chloride and sulfuric acid-chloride because the velocity of groundwater in the area is almost stagnant.
In
the north, east and southwest of Taiyuan basin and In the loess hills ,loess 台塬, skirt of proluvial fan and part
of Dip plain, and in the both sides of Fenhe River Fenhe River from Lanbun to
Sangei and from Xizhai to Sunjiazhai ,the mineralization of water was less than
1 g/l and the water
quality was passable and the Type of water chemistry HCO -Ca. Mg or HCO3-Ca.
Na because of the recharge of precipitation and fresh water from bedrock at
Bianshan and and a short avenue of runoff and fluvial diluting effect.Affected by upper shallow pore water, the
content of Na + is on the high side and the Type of water chemistry is HCO3Na
.Ca or HCO3—Na. In the area from the south of Sangei village,
From part of the lower part of the dip plain to the alluvial plain , the type of water chemistry is HCO3 ,mineralization of water is 0.4—1.26g/l;in some area ,the Type of water chemistry is SO4Cl· HCO3 or Cl· SO4 or SO4 ,for example, the type of water chemistry is SO4Cl· HCO3 --Mg·Na(Na) and the mineralization of water 1.37—2.43g/l and the total hardness 650—700mg/l in Taiyuan Wusu,Qingxu Echi,and the type of water chemistry is Cl·SO4--HCO3 --Ca·Na (Na) and the mineralization of water 1.25-2.91g/l and the total hardness 518-- 2139mg/l in Taiyuan Wujiazhuang,Nanheiyao.and the type of water chemistry is SO4-- Ca·(Na) and the mineralization of water 1.25-1.54g/l and the total hardness 843.2 --851mg/l and the water quality is bad in Dongzhuang district Taiyuan Jinyuan and Wu Village Qingxu. In these area such as the middle part of the basin,Xiaodian,Wangda,Xigu,south of Baijiazhuang village, Hongshan,Dujiazhuang village, Yanwu,Yanguotou etc,Sealed-in water and the mineralization of water is 1—3g/l.This is because the pore water in the middle or deeper layer has the character of confined water and semi-confined water and the pore water in this layer is recharged by surface runoff and part of part of atmospheric precipitation just at the top of the Bianshan proluvial fan and basin around. The ground water recharged runs off toward centre of the basin and dissolves out a large quantity of salt during its flow process because the ground water flows particularly slowly.At the bottom of the basin ,because artesian head is high;besides, the runoff is slow;there is a vertical alternating movement as well.and the precipitation is mainly consumed in land evaporation and there is only a little inleakage particularly in the dry season because the temperature in the basin is higher .Moreover ,because it is affected by human factor and the discharge of industrial sewage and domestic sewage and sewage irrigation and mixed exploitation of pore water in shallow and middle or deeper layer and the leaking recharge of shallow seated groundwater to pore water in middle or deeper layer. All these reasons stated above cause the complication of types of ground water.
3.2 Formative factor analysis of quality of groundwater
The formation and variation of phreatic chemical composition is constrained by many factors which can mainly be summarized as properties of water-bearing media (rock composition), conditions of recharge, runoff and discharge of ground-water, evaporative concentration and human factors.
3.2.1 The effect of water-bearing media character
Groundwater exists and translates in water-bearing media which is pore and cranny. Groundwater dissolves the dissolved salt in the rock and becomes the solution that comprises of ion、molecule、colloform、air and so on. For example, the stratum of Cambrian Ordovician comprises of limestone and contains higher salt of calcium and magnesium, so the kind of groundwater contains higher ions of calcium and magnesium. Coal stratum of carboniferous system contains higher sulfide, so the cranny water in the stratum of clastic rock and carbonate rock form the sulfuric acid water of weight carbonic or the weight carbonic acid water of sulfuric. The sandrock of clastic rock are feldspar quarta sandstone and contain more plagioclase, so the ions of calcium and natrium are higher in the fissured water of clastic rock. Also, the limestone of Fengfengzu in Ordovician contains mass gypsum interlayer. When Fengfengzu lies under the groundwater, dissolution of gypsous makes the quality of karst water deteriorate, and water turns from the weight carbonic acid water to the weight carbonic acid water of sulfuric or the sulfuric acid water of weight carbonic.
3.2.2 The condition of replenishment, flowthrough and drainage and the influence of evaporation and concentration
The condition of replenishment, flowthrough and drainage of groundwater has effect on the accumulation of salinity in the groundwater and transformation of hydrochemistry type. The groundwater in mountainous area commonly has much bicarbonate (carboniferous coal bed exception). The quality of cranny water in drossy terrane is worse than the one in regolith. In the loessial hill and middle-top area of diluvian pie slice, the quality of the groundwater is better because water table is imbedded deeply and the formation of groundwater is mainly dissolving and filtration. In the center of basin or diluvian connect billabong area ,the grain of hydrated bed is thin,and the route of flowthrough is longer, water table is imbedded shallowly,and the condition of flowthrough is bad,so evaporation and concentration have much effect and the quality of water is worse. Middle and deep bed water in basin mainly accept mountainous's groundwater's side replenishment, and accept shallow groundwater across replenishment , so mountain side basin terrane groundwater's quality and shallow groundwater's quality have much effect on middle-deep groundwater's quality.
3.2.3 The influence of the factitious factors
The influence is mainly three wastes, domestic sewage and sewage irrigation. They not only pollute the groundwater but also deteriorate water quality, so fresh water resource reduces. They have the bad effect on the people’s life and they are important factors affecting the water quality of shallow groundwater.
3.3 The space time evolvement of geochemistry surrounding of basin groundwater
3.3.1 Shallow pore water
The quality of shallow pore water in basin is chiefly controlled by water-bearing media’s property, depositional environment, climate and patch track exhaustion, so it offer visibie diapason variation regular pattern. From basin margin to basin center, the degree of mineralization increases and water quality deteriorates.
In basin north, hill and
mountainside limon rolling country, the quality of shallow pore water is
accepted by human factor faintly and water quality is relative steady. For
example, in xiangyangdian, beixiawen(
Variation regularity of pore water quality in semideep stratum is similar to shallow pore water. In other words, pore water quality in semideep stratum changes regularly from basin margin to basin centre. Water quality of basin margin is superior to the one of basin centre and water quality of the north is superior to the one of the south. Water quality is consistent with the direction of groundwater flow. Figure 11 shows that the direction of groundwater flowthrough in the south of the basin isLuoyangcun-Guxianzhen–Xiashen –Nangufeng. Along this direction, TDS of water, total hardness, SO42- and Cl- gradually increases. Variance of hydrochemistry ingredient reflects the direction of groundwater flow.
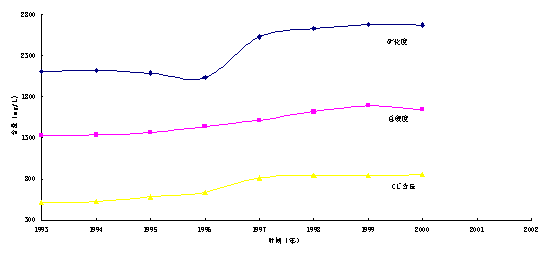
Figure10 Change chart of mineralization of water, total hardness and content of chloride ion in the water head site of chemical plant
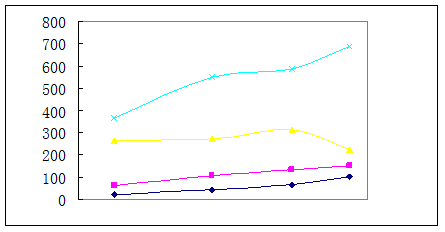
Figure11 tendency chart of groundwater ingredients with spatial variation
The
hydrochemistry type of semideep stratum pore water is more steadier than the
one of shallow pore water and the variation of the type is small. Especially in
the alluvial fan area and clinoplain area, the condition of groundwater runoff
is preferable and the hydrochemistry type is steady for many years, such as the
north of Xincheng,
mineralization increases slowly because local area suffers pollution
from shallow pore water, such as Wujiazhuang in
By contrasting the variety hydrochemistry field of basin in 1983 with 2003, it is found that hydrochemistry type of semideep pore water trends to be simple, especially in the middle of basin the variety is obvious. At present the type is H.S and H.C, but in 1983 it is H.S、H.C、S、S.H、S.C、C.S、C.H and so on.
The area in which TDS is 1 to 3 g/L is 1657 km2 and the area in which TDS is 3 to 5g/L is 40 km2 in 1983. The area is 895 km2 in 2003 and TDS is smaller than 3g/L.
It shows that exploition and
utilization of groundwater resources in
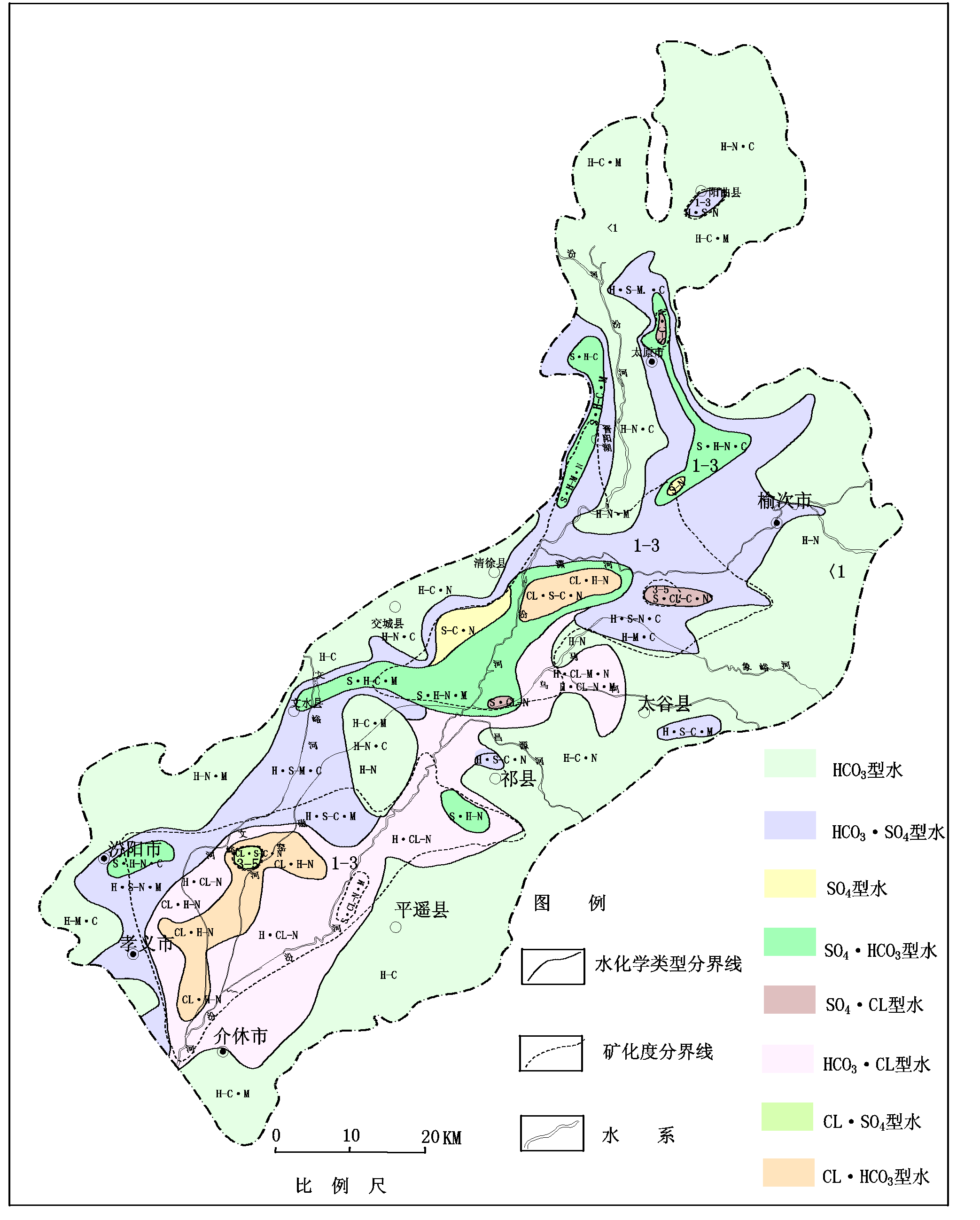
hydrochemical map of
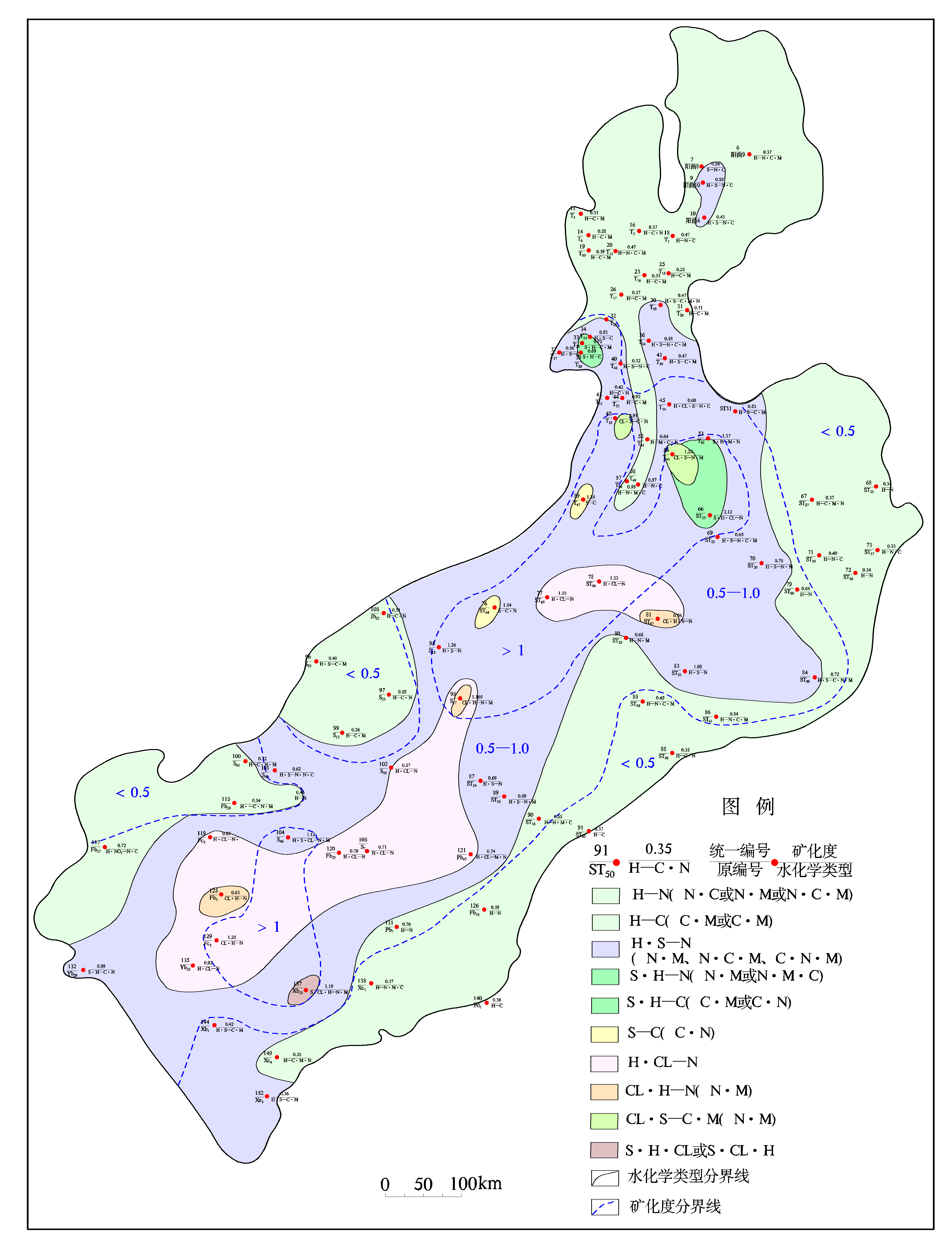
hydrochemical map of
References:
[1] Zhangzonghu and Shenzhaoli. ‘Environmental evolvement of groundwater in North China Plain’,Peking,Geological publishing house,2002,vol.2.
[2]
Liangwenbiao and Lihongjian. ‘Taiyuan basin margin topograph and new tectonic movement
and its meaning’,
[3]
Geology mineral bureau in
[4]
Wangyanxin,Guohuaming and
Yanshilong. ‘Environmental evolvement of shallow pore water groundwater system
and analyse of pollution sensitivity-Datong basin in
[5] Liwenpeng and Haoaibing. ‘Cognition about groundwater resources in arid region of our country’, Hydrogeology and engineering geology, vol.5,1996.




