Achievements
THE ANALYSIS OF HYDROGEOLOGICAL-ENVIRENMENTAL PROBLEMS AND DIVISION OF PROTECT REGION IN SHANXI KARST SPRING AREA
Liang Yongping, Han Xingrui, Yi Lianxin, Wang Weitai
Karst Geological Institution Of Chinese Geological Academy
Abstract: The article aimed at Shanxi karst springs'discharge seriously decay in recent years, according to the water resource theory, through the research of the 18 karst spring areas'(Fig-1 Jinci spring area, Lancun spring area, Shentou spring area, Niangziguan spring area, Xin’an spring area, Guozhuang spring area, Pingshang spring area, Majuan spring area, Longzici spring area, Huoquan spring area, Sangu spring area, Yanhe spring area, Tianqiao spring area, Liulin spring area, Gudui spring area, Hongshan spring area, Shuishengtang spring area and Leimingsi spring area, )water resources system structure model, the constitution of water resource elements and the circulatory process. Analyse the springs' frangibility and why the springs' discharge was decay from two aspects: natural and artificial.And then take this as a foundation footing and protect the springs as a intention.According to groundwater exploitation and coal mine exploitation affected to the sensitivity of springs' discharge, divided the spring area into several protect regions with different rank,and also put forward different protective suggestions to every different rank.
Key words:
ⅠTrend and Reasons of Discharge Decay

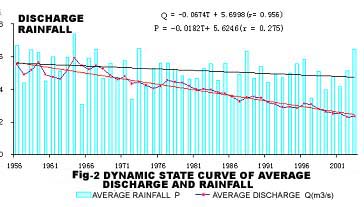
Fig-2 was a dynamic state curve of the 15 karst springs’ discharge in Shanxi province.the graph shows us that:from 1950s to the middle of 1960s, discharge had been fluctuated horizontally, but after the middle of 1960s, this data appeared a obvious decay tendency.The discharge of the 15 springs had been decreased gradually with the speed of
Why all these springs discharge were decayed can conclude into the following reasons:
1 Precipitation amount was decreased and evaporation on land was increased
By the contrast between the two stage in 156 precipitation station belong to the 18 springs.Compared with the first stage, all the springs universally decreased 3.5-14.38%,and the total average evaporation reduced 8.26%.According to temperature data and use Turkˊs empirical formula about evaporation on land: because of temperature-increase leads to penetration decreased amount was about to 49%.
2 Influence go with exploit karst groundwater in spring area
By the karst-groundwater exploitation quantity data in 16 spring areas(except the quantity in the spring head), the average exploitation quantity was
3 Water-sourroundings change affected to discharge
Most of
4 Use of land
Exploitation of coal mine were universal among all the spring areas, large-scale exploitation have last more than 20 years not only change runoff producing condition on the ground surface,but also destroyed the clastic rock aquifer’s system structure in spring areas. According to the water resource evaluation report(the 2th time):the variety of the hydro-underlying-bed was the most important reason led to the decay of river runoff quantity in
Ⅱ Frangibility analysis of the springs’ discharge
1 The water resource system characteristics of karst-spring area in
To understand the water system characteristics from system angle, karst-spring areas in
Karst-groundwater system here is integrated and cosmically. The karst-groundwater aquifer in Shanxi constitute mainly by continuous deposit, very thickly carbonate rock (normally with a depth of 700~
The karst-groundwater system has lots of water resource elements and the conversion relations among the elements were complex: Most of the system exist atmospheric precipitation, surfacewater, loose alluvium pore groundwater, slastic rock crevice groundwater and karst groundwater, etc at the same time. And there are different kinds of complex conversion relation among all these water resource types, it made factors that affected karst groundwater increased and water surroundings quality frangibility.
A karst spring field always belong to differenf distracts (different country,city or province ) and different water user at the same time. And several kinds of intake projects functioning parallel increased difficulties to admeasurement and management of water resource.
Most of
2 The water resource system structure type and characteristics of the spring areas in
The hypsography of
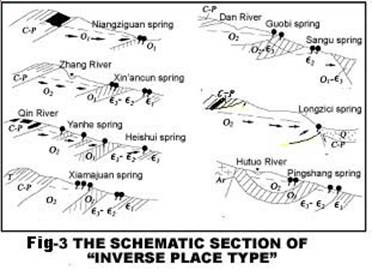
According to the system structure of karst groundwater and relations between karst aquifers and the stream set of groundwater.We divided the karst water resources into three types: “ Inverse place type”, “Fluently place type” and “others”
(1); The system model of “Inverse place type” .
This kind of model mainly distributed at Taihang mountain area on the southeast of Qingshui syncline and a little distributed at the southeast and southwest of Lvliang anticlinorium. The mainly characteristics of this type were:
1> The whole stream set of karst groundwater was rightabout to the aquifer dip.The dominating regional geological structure was spring area located at one side of the syncline.Because of the central of syncline aquifer which cover up deeply cause groundwater movement suffocating. Consequently, the groundwater movement was converse to the tendency of stratum,and drained at the place where have appropriate geological and topography conditions.
2> The late Paleozonic Era and Mesozonic Era clastic rock stratum distributed at the up stream of the groundwater system. The mainly nourishment source of karst groundwater was composed of surfacewater that originated from these clastic rock area.
3> The groungwater recharge area distributed at the lower reaches of the spring,and enriched at the shallow department where the Ordovician and the coalsystem stratum get in touch with,and here always formed surf-runoff zone.
4> The drainage of groundwater was formed because of water-tighting of regional confining bed. Especially for the reason that the relative insulation by limestones at the bottom of middle series of Ordovician system and under Ordovician system series, The distribution of springs were disperse.
(2); The system model of “fluently place type”.
The water resource system of this model mainly distributed at the east of Lvliang mountain,the edge-mountain of the rift basin in Fenwei graben,the southeast of Lvliang mountain anticlinorium.The mainly characteristics of this model were:
1> On the transerve section,the move direction of groundwater was congruously with the stratum incline.Its geological structure foundation was groundwater circulated in amonocline on one side of the anticline.
The late Paleozonic Era and Mesozonic Era clastic rock stratum distributed at the downstream of the groundwater system. So, there always spreaded artesian areas of karst groundwater.
2> Karst groundwater can be enriched at the shallow department where the Obdovician and the coal system stratum get in touch with, the spring outlet before the breakage which on the front of mountain and artesian areas of downstream of spring outlet.
3>The draining of karst groundwater was formed because of the water-tighness of regional confining overlying beds or stratums under the breakage structure .
(3); “Others” model.
Other three spring areas: Gudui spring area, Shuishengtang spring area now can not be classified into any of the model. So, for the moment, we called it “others” model.
3 The analysis of influence factors to the karst spring’s discharge frangibility
The concept of trangibility to groundwater system was put forward for evaluated the capability that water-bearing system resisted contamination.The spring’s discharge frangibility we discuss today was put forward under the serious situation that karst springs in Shanxi were in the face of discharge decay or even setting off,and how to protected it under this situation. Any spring, when its recharge-didischarge was out of balance for a long time, setting off of the spring will be the logical result. But the development scale, structure of stratum, type of water-bearing media and the spring’s formation conditions of the water resource system was so different, and distribution, buried conditions,rules of enrichment and flow speed of karst groundwater were also different with each other. There are always zones in some spring that their discharge response mightness towards outside functions. The influencing pace and intensity were visible when exploited karst groundwater in these places.Especially in some sensitive places,a number of wells may cause the spring made a completely move.So,we defined the frangibility of spring discharge in spring area as: the sensitivity degree of spring discharge in spring area to outside force under the influence of outside environment. The discharge of the spring more frangibility means that the spring was more and easily affected by the influence of outside activity. The mainly conditions that affected the discharge frangibility of spring were:
1 The spring area growth scale is small and supply resource amount is limited, a little amount of mine may cause the spring dried up. Such discharge of spring areas is tender.There are
2 There are artesian provinces of karst groundwater enrichment zone, and less enrichment zone of artesian coal mine area. Dill wells to get water at these place equal to incerpted spring water directly,it will leads to discharge decay easily.And excavate mine in the artesian coal mine area,once coal mine suddenly occur declogging will cause discharge decay directly too. Spring areas with such characteristics were: Liulin spring area, Tianqiao spring area, Hongshan spring area,Jinci spring area, Leimingsi spring area, Guozhuang spring area,Huoquan spring area, and these spring areas were all “ fluently place thpe” system model.
3 The discharge of spring areas controlled by fracture zones. Although these fractures have water-tighness on its transverse section,but in
4; Strong-runoff zones of karst groundwater was developed .The karst growth degree was deficient in Northern China,But in some large-scale spring areas, through a very long time karstification,affected by the following factors:the lithology of aquifer,structure, environmental geology background,ancient karst,hydrodynamic and other influencing factors,finally formed strong-runoff zones of karst groundwater. These strong-runoff zones had such characteristics: transmissibility was relatively better,water volume was abundant, single well has agreat water crop,and reflected in the chart of hydroisobathwas a flute.Some large-scale runoff zones even with a length of several ten kilometers long. and connected directly with the spring out let.So,when exploited karst groundwater in the strong-runoff zone,there will be obvious infection to the discharge of fountain.By prospecting and analyse the hydroisobath,it can be affirmed that spring areas with strong-runoff zones include:Niangziguan spring area,Xin’an spring area , Sangu spring area, Yanhe spring area,Jinci spring area, Tianqiao spring area,Liulin spring area, Guozhuang spring area and Shentou spring area.
5: The centralized degree of the fountain discharge.
Table-1 Analysis table for single factors of frangibility
SPRING AREA | TYPE | SCALE | GRAVITY FLOW | FRACTURE ZONE | STRONG RUNOFF ZONE | DECENTRALIZATION |
Niangziguan | INVERSE PLACE TYPE | large | nonexistence | no | have | dispersed |
Xinan | large | nonexistence | no | have | dispersed | |
Yanhe | middle | nonexistence | no | have | dispersed | |
Sangu | middle | nonexistence | no | have | dispersed | |
Pingshang | middle | nonexistence | no | unknow | dispersed | |
Majuan | small | nonexistence | no | unknow | dispersed | |
Longzici | middle | nonexistence | yes | unknow | centralized | |
Shentou | FLUENTLY PLACE TYPE
| middle | existence | yes | have | dispersed |
Leimingsi | small | existence | no | unknow | dispersed | |
Lancun | middle | existence | yes | none | centralized | |
Jinci | middle | existence | yes | have | centralized | |
Hongshan | small | existence | yes | unknow | centralized | |
Guozhuang | large | existence | yes | have | dispersed | |
Huoquan | middle | existence | yes | unknow | centralized | |
Liulin | large | existence | no | have | centralized | |
Tianqiao | large | existence | no | have | dispersed | |
Shuishentang | OTHERS
| small | nonexistence | yes | none | dispersed |
Gudui | small | nonexistence | yes | unknow | centralized |
The formation reasons of karst springs in
Marshal the influencing factors of discharge frangibility in the Table-1,we can conclude that the discharge frangibility of water resource system in “inverse place type” was lower than the type of “fluently place type”.
Ⅲ Partition of the protection regions about fountain discharge
The aim to protect the discharge of fountain was to maintain the spring output on a certain amount, that the amount could be able to satisfy the water supply need,at the same time, the amount could also bring into play its tour, ecology and other functions. Consequently, in the process of development and programming, we should take the exploitation amount of resources as a foundation, practice a total amount control, play discharge of spring and exploitation amount of karst groundwater in different region belonged to the same spring area as a whole.According to the characteristics of different spring areas,divided protection regions of fountain discharge as the following Table-2and Fig-5.
1 Protection regions of spring head
Protection regions of spring head means drainage districts of karst groundwater which was revealed. The total area of the 18 protection regions of spring head divided this time was

water supply establishment and protect the spring head should not br set up lately,rebult and enlarged. Advocate to get water by collect fountain instead of drilling wells in the spring head.Strengthen the protection of natural sight and historic architecture in the spring head.
2 The first-rank protection region in spring areas.
The first-rank protection region in spring areas were mainly aimed at places where are sensitive to the influence of discharge. These regions include: fracture zones in front of mountain which formed springs, artesian regions under the spring outlet which were closely related with discharge of springs, strong-runoff zones of karst groundwater which discharge amount approach to minimum target value. There are 11 among all the 18 spring areas exist prior-protective regions of water quality. The total area is
Table-2 Area statistics of protect regions (km2)
ITEMS
SPRING AREA | TOTAL AREA | SPRING HEAD | FIRST RANK | SECOND-RANK | SUBLAYER-COAL BEARING COURSE REGION |
JINCI | 2030.00 | 2.06 | 183.35 | 243.46 | 601.76 |
LANCUN | 2500.00 | 3.77 | 178.88 | 73.91 | 76.05 |
NIANGZIGUAN | 7226.72(9.72) | 13.87 | 222.05 | 1107.95 | 2544.68 |
XINAN | 10950.00 | 16.07 | 0.00 | 1627.00 | 6826.19 |
SHENTOU | 4756.00 | 10.18 | 43.53 | 349.79 | 842.85 |
GUOZHUANG | 5600.00 | 9.33 | 374.48 | 1387.29 | 1363.49 |
GUDUI | 460.00 | 5.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92.60 |
LIULIN | 6080.54(78.05) | 2.08 | 221.7(51.61) | 261.55 | 1595.27 |
YANHE | 2765.00 | 40.04 | 0.00 | 284.20 | 642.71 |
SANGU | 2630.00 | 27.31 | 178.80 | 391.45 | 97.79 |
PINGSHANG | 3035.00 | 10.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
MAJUAN | 754.00 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 44.96 | 239.46 |
TIANQIAO | 13591.48(3399.48) | 33.86(11.34) | 0.00 | 17.13(4.47) | 808.46 |
HONGSHAN | 632.00 | 1.92 | 70.10 | 82.30 | 72.82 |
LONGZICI | 2250.00 | 11.20 | 19.90 | 24.87 | 0.00 |
HUOQUAN | 1273.00 | 2.30 | 35.49 | 1235.21 | 199.79 |
SHUISHENTANG | 518.00 | 9.24 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
CHENGTOUHUI | 1672.00 | 13.68 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
LEIMINGSI | 377.00 | 22.85 | 51.69 | 228.89 | 28.13 |
Σ | 67428.74(3487.25) | 222.58(11.34) | 1579.97(51.6) | 7359.96(4.47) | 16032.05 |
Note: in()was area out of shanxi provinceⅣ
region include: Except the situation that water is used by people and livestock drinking or other spectial use,and there are not other water sources.
exploitation wells and exploitation amount pertinent to karst groundwater and pore groundwater in loose layers which have close relation to karst groundwater should not be set up lately. For the water sources have already established,we should gradually decrease the exploitation amount if there are substitutable waterhead. Coal mining under the karst groundwater level should be sternly controlled in the protection region.
3 The second-rank protection region in spring area.
The second–rank protection region mainly aimed at strong-enrichment zones of karst groundwater (strong-runoff zones, water-collecting region )and the whole distribution region of karst groundwater in some spring area which needs spectial protect.Karst groundwater in these places are abundant,single-well has great water crop and transmissibility was relatively better.Dill wells at these places will leads to great
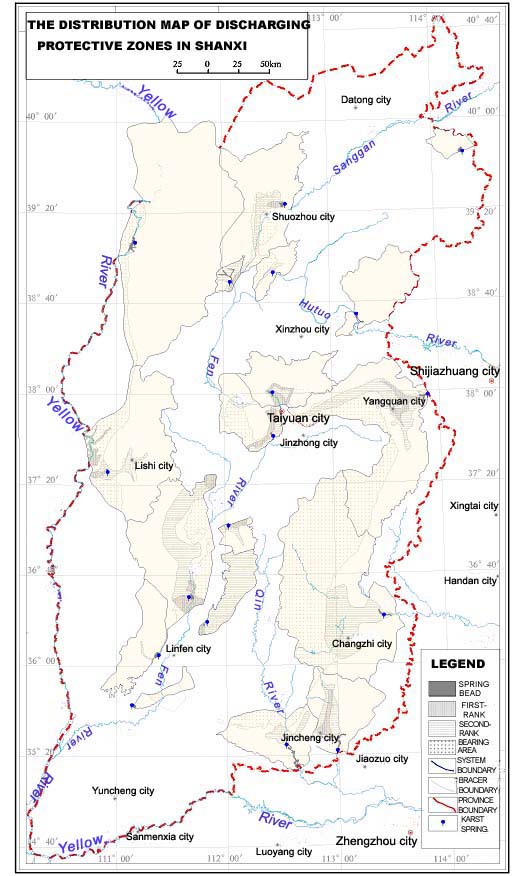
Fig 5 The distribution map of discharging protective zones in
influence to the amount of discharge, and the respond of time was quickly.
There are 15 among all the 18spring areas exist limited protection regions of water amount.The total area is
4 The region in coal mine that its sublayer-coal is bearing course
Regions that the distribution of sublayer-coal under the karst groundwater level in spring area. There are 15 among all the 18 spring areas exist such regions (a part of Tianqiao spring area that out of Shanxi is lack of credible date ).The total area is
Conclusions
Karst springs in
Acknowledgement
This article was supported by “KARST AQUIFER AND WATER RESOURCE” (IGCP513) project which was supported by UNESCO and IGU.




