Achievements
THE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES DISTRIBUTION AND ITS EXPLOITATION AND UTILIZATION IN HUANG-HUAI-HAI PLAIN
Jing Jihong1, Jing Lei2, Sun Jichao1, Wang Shan1
1.
2.Owens
Abstract: The groundwater resources distribution and its exploitation & utilization in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain were described in the article. Each district’s exploitation and utilization degree on groundwater resources were presented, and over- exploitation or exploitable potential in different districts also was explained. It provided some scientific basis for reasonable developing and using groundwater. Last, some trouble in the course of exploitation was showed up and some advice for sustainable development was given.
Key words: Distribution Feature, Groundwater Resources, Nature Recharge Resources, Exploitable Resources
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is located in the east of China, 113º—121º30´ E,32º—41º N, on the west of Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, east of Taihang Mountain, Funiu Mountain, and Dongbai Mountain, south of Yanshan Mountain, north of Dabie Mountain, Huaihe River and Subei Irrigation Channel, about
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is deposited by Yellow River,
1 General Situation of Water Resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
Climate of the plain is semi-warm, semi-humid & semiarid, annual average rainfall amount about 500
Nature recharge resources for groundwater is
Groundwater is the most important water supply resources, exploitation amount is
2 Distribution Feature of Groundwater Resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
Groundwater distribution presents well-regular on horizontal plane. From the plain nearby mountain to middle plain to coastal plain; the aquifer components from coarse particle diluvium to coarse-middle-fine particle diluvium to fine-coarse diluvium; groundwater flows from powerful flow to weak flow to stagnation; water-yield of aquifers from rich to secondary to weak; types of water chemistry from hydrocarbonate water to sulfate water to chloride water; and mineralization degree from small to big, namely from fresh water to brackish saline water to saline water.
From aspect of nature recharge resources modulus to analyze, groundwater yield has regional difference obviously (Figure 1). From high to low in turn, the modulus is:

Fig.1 Nature recharge resources modulus of groundwater in each district
Natur![]() e recharge resources of fresh groundwater is 342.73×
e recharge resources of fresh groundwater is 342.73×
Nature recharge resources of different mineralization degree types within each district are showed in Figure2. Content of brackish saline water and middle saline water within groundwater resources
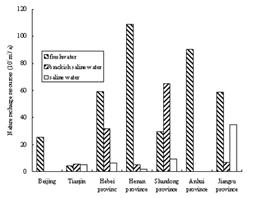
Fig.2 Nature recharge resources of groundwater in each district
is the highest in Shandong province and Tianjin, it is 71.8% and 71.6% respectively, secondarily is Hebei province and Jiangsu province, which content is 39.5% and 34.5% singly.
3 Current Status of Groundwater Resources Exploitation and Utilization in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
3.1 Exploitable groundwater resources amount
Assessment area on exploitable fresh groundwater is
From Figure3,
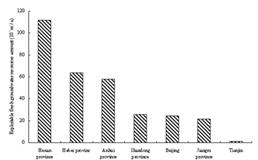
Fig. 3 Exploitable fresh groundwater resources amount in each district
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is the highest plain region in
3.2 Exploitation degree of ground-water resources
According to the statistic data from the city and county within the plain, exploitation degree of groundwater resources could be classed as 7 levels, namely >120%, 100—120%, 80—100%, 60—80%, 40—60%, 20—40%, and <20%. Exploitation degree of the cities and its distribution are listed in Table-2 and Figure-4. From the table and figure, exploitation degrees in different districts are various obviously. Over exploit seriously in
3.3 The proportion of groundwater resources within water supply
The proportions of groundwater within water supply in each district are showed in Table3.
The cities’ quantities are listed in Table4 by proportion of groundwater within water supply amount and the purpose of groundwater.
Table1 exploitable brackish saline water and middle saline water resources amount within each district Unit:
district | Brackish saline water | Middle saline water |
2.86 | 2.57 | |
20.19 |
| |
5.44 | 1.68 | |
55.17 | 7.48 | |
1.67 | 9.97 |
Table2 the city quantities’ distribution by exploitation degrees of groundwater resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
District | Exploitation Degree(%) | ||||||
>120 | 100—120 | 80—100 | 60—80 | 40—60 | 20—40 | <20 | |
1 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
|
|
| |
3 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
|
| |
52 | 30 | 12 | 13 | 5 | 1 |
| |
13 | 9 | 7 | 13 | 16 | 6 | 12 | |
31 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 7 | 3 | |
1 |
|
| 2 | 3 | 10 | 9 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12 | |
Table 3 Water supply amount in each district within Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, 1999
District | Groundwater supply amount ( | Surface water supply amount ( | Other water supply amount ( | Total water supply amount ( | Proportion of groundwater supply in total water supply (%) |
149.46 | 50.90 | 0.72 | 201.08 | 74.3 | |
27.15 | 14.95 |
| 42.10 | 64.5 | |
129.72 | 95.60 | 0.28 | 228.60 | 56.7 | |
122.99 | 135.87 | 2.56 | 261.42 | 47.0 | |
6.33 | 18.44 |
| 24.77 | 25.6 | |
18.48 | 175.22 | 0.36 | 194.06 | 9.5 | |
18.34 | 422.03 |
| 440.37 | 4.2 |
Note: the data of surface water supply amount from Ministry of Water Resources
Table 4 the city quantities’ distribution by proportion of groundwater within water supply amount on industry, agriculture, and living
Purpose | Proportion of groundwater within water supply amount | |||
>80% | 50—80% | 30—50% | <30% | |
Industry | 21 | 12 | 1 | 13 |
Living | 27 | 12 | 2 | 6 |
Agriculture | 4 | 16 | 11 | 16 |
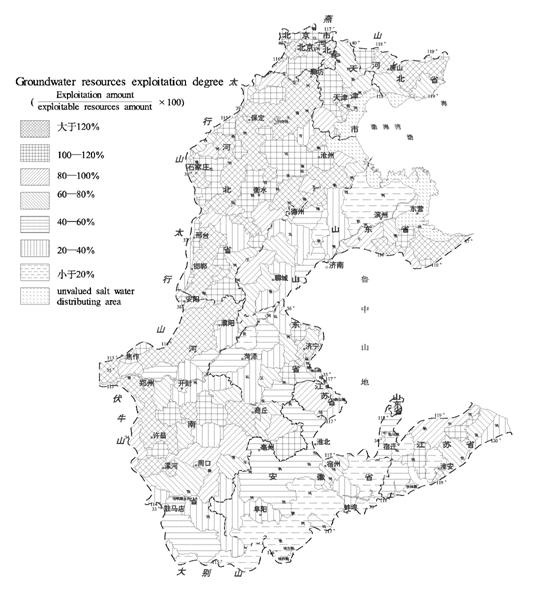
Fig. 4 Current status of exploitation and utilization ofgroundwater resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
4 Analysis on Exploitable Potential of Groundwater in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
Exploitable potential not only is residual of exploitation which can be got, but also include new finding resources by work hard. Therefore, to comprehend exploitable potential of groundwater should be analyzed with developmental point of view.
4.1 Current annual residual amount of groundwater exploitation
It is only an average outcome to analyze exploitation potential in provincial district, which stay on the surface, and can not reflect the fact of potential. Groundwater is a kind of regional resources, over exploitation and remains coexist within a region frequently, thus province’s average outcome maybe cover up regional over exploitation or exploitation remains. Therefore, the analysis of groundwater potential should be carried out within small hydrologic regionalization or small district. From Table-5, Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei province, all are over exploitation, have been without exploitation potential, Shandong’s exploitation potential is very small also. The districts with high exploitation potential are on the south of the plain. But from Table-2, which statistics according to cities or counties, there are lots of counties with exploitation potential within each province.
Table 5 Residual amount of fresh groundwater exploitation in the provinces or municipalities within Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
District | Exploitable resources amount ( | Current exploitation amount ( | Residual amount ( |
26.33 | 27.15 | -0.82 | |
5.70 | 6.33 | -0.63 | |
99.54 | 127.50 | -27.96 | |
80.68 | 18.34 | 62.34 | |
135.21 | 18.48 | 116.73 | |
114.31 | 107.30 | 7.01 | |
155.89 | 129.72 | 26.17 | |
Total | 617.66 | 434.82 | 182.84 |
Note:
4.2 Annual increasable exploitation amount by strengthening management and mending technical
Brackish saline water and middle saline water can be utilized in irrigation and partial industry, and there are lots of successful examples, which partial solved local absence of fresh water resources. According to primary estimate, 86.43×
4.3 Annual increasable exploitation amount by investigating
4.4 Reserved exploitable deep confined water resources could be treated as emergency water resources
Exploitable amount of deep confined water resources is composed by leakage recharge of confined aquifer under exploiting condition, lateral recharge and consumptive storage. According to primary estimate, exploitable amount of deep confined water is 110.0×
At present, except Hebei Plain,
5 Advice for sustainable development and utilization of groundwater resources
Rational plan exploitation according to groundwater resources and environmental carrying capacity. Act according to actual circumstances;2.Save groundwater, and increase utilization ratio;3. Protect groundwater from pollution;4.Exploit potential by adjusting measures to local conditions and find new groundwater resources; 5. Found groundwater reservoir, and realize united control for surface water and groundwater.
Reference
[1] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(colligated report), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[2] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources and environment atlas of
[3] Zhang Zonggu, Lu Yaoru, water resources development and utilization in West China, China Water Power Press, 2002
[4] Chen Mengxiong, Ma
[5] Huang-Huai-Hai Plain’s hydrogeologic assessment team of Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of PRC, Hydrogeologic assessment of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, Geology Press, 1992
[6] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Beijing), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[7] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Tianjin), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[8] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Hebei), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[9] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Jiangsu), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[10] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Anhui), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[11] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Shandong), Sinomaps Press, 2004
[12] Zhang Zonggu, Li Lierong, Groundwater resources of China(Henan), Sinomaps Press, 2004




