Groundwater Quality Safety and Contamination Recovery
DISTRIBUTION CHARACTERISTICS AND COUNTERMEASURES OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY PROBLEMS IN THE HUANG-HUAI-HAI PLAIN
Li Zhenghong1 Sun
Jichao1 ZhangSheng1 WangShan1 Guo
Xiuhong2,1
1 Institute of
Hydrogeology & Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of
Geological Sciences Shijiazhuang 050061;
2 School of Water Resources
and Environment, China University of Geosciences , Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract:About 20 years of
the researches on hydrogeology, environmental geology, groundwater dynamic
monitoring, environmental monitoring are used to assess the environmental
geology problems in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain, which have resulted from the
irrational groundwater exploitation. The relevant countermeasures have been
proposed for protection and control of the environmental geology problems. The
assessments show that groundwater over-exploitation (maximum 363.11%)
constantly is the reason that has induced the environmental-geology problems
such as the regional depression cone, land subsidence, geo-fissures, land
collapse, seawater intrusion, salinization and groundwater contamination in the
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. The big regional complex depression cones have been
formed in the plain. There are over 20 big depression cones that have caused
land subsidence, geo-fissures and land collapse. Groundwater contamination is
mainly from the shallow groundwater in a form of point and linear only partial
plane distribution in the plain where 29 cities are suffering from
contamination such as Beijing, Langfang, Tangshan, Cangzhou, Suxian,
Fuyang, Liaocheng, Dezhou and Dongying. The main excessive components are TDS、NO3-、NO2-、NH4+、F、Cl-、Fe、Mn.
Keywords: Environmental-geological
problems, countermeasures, Huang-Huai-Hai Plain
The Huang-Huai-Hai
plain includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong, Henan, Anhui and Jiangsu,
covering an area of 28.5×104km2. It is also one of the
important industrial and agricultural bases but lack of the surface water
resources. Groundwater resources are of importance in economic and social
development in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain. With social economy development, human
activities for exploitation of groundwater are aggravating day after day, while
environmental geology problems relate to groundwater have severely influenced
social and economic development, even life of the local people. Groundwater
estimation on environmental geology problems made a significant sense to know
the real situation, to protect and improve ecological environment and to
advance society and economy sustainable development in the
Huang-Huai-Hai plain.
1Characteristics
of the Natural Environment
The Huang-Huai-Hai
Plain covers an area south of the Yanshan Mountains and east of
the Taihang Mountains and north of the Dabeishan Mountains,
including the Haihe and Luanhe alluvial-proluvial plain, the Huaihe plain and
the panplain of the Yellow River, and goes down from west to east towards the
Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea like a dustpan. The Yellow
River is taken as the boundary of Climate in this region that there is a
great difference between the south and the north. The arid climate is
predominant in the north part, the annual precipitation 500~600mm/a, and less
than 500 mm/a in some area, the aridity 1.5~2.0; but in the south there is
a warm-subhumid region, the annual precipitation 600~800mm/a, the aridity
1.0~1.5. The dense population, the industry and agriculture developing rapidly
have made the water resources comparatively lack with the specific climate
conditions in the region. Especially in recent years,the urbanization has made the issue even
worse for the demands of water supply are increasing swiftly. Now the
Huang-Huai-Hai Plain has become one of the most regions lacking water resource
in China.
2 Environmental
Geology Problems Induced by Unreasonable Groundwater Exploitation
In recent years, over-exploitation of groundwater is increasing day by day
in order to meet the need of the economic development, by which Groundwater
resources have been aggravated with occurrence of a series of environment
problems, such as the regional depression cone of groundwater, land subsidence,
geo-fractures, land collapse, sea water intrusion, salinization and groundwater
contamination etc.
2.1 Depression cone enlarged by constant drawdown of the
regional groundwater level
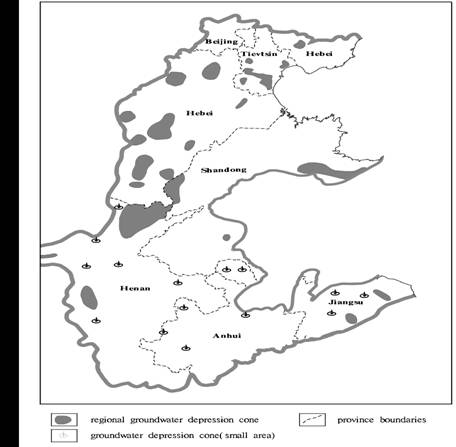

The depression cone is one of the most serious problems in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in china. The statistics show that the exploitation over 60×108m3/a in 1980s to 1990s broke the equilibrium of groundwater. The shallow groundwater level went down to form 20 big depression cones (depression cone area over 100km2) even in the piedmont area where groundwater intensive exploitation as the well fields could also form the depression cones over the mid-south of Tianjin, Tangshan, Bazhou, Baoding, Cangzhou, Shijiazhuang, Xinji, Ningjin and Xingtai in Heibei Province, Dongying and Jining in Shandong Province, Puyang and Xuchang in Henan Province, Huai’an and Binhai in Jiangsu Province (Fig.1). The situation tends to be from point to area, from the urban area to the countyside, from shallow aquifers to deep aquifers. The aquifer depletion becomes more and more serious and the environmental problems may take place as the land subsidence. The measures have been taken to control over-exploitation of groundwater since 1985 from 1985 to 1999. The result was about 2m/a recovered(as the deep groundwater depression cone at Hengshui). The development of depression cone tends to be reduced at present.
2.2 Land
subsidence
Overexploitation
of groundwater, especially the concentrated well fields’ pumping, has caused
the constant drawdown of the regional groundwater level accompanied with the
lacunaris media compact and the land subsidence. It appears at the eastern
suburb in Beijing, such as Changping, Shunyi, Fengtai, Tongzhou and Daxing
etc. It is over 1800 km2. The subsidence has distributed in
Hebei Province such as Changzhou, Baoding, Hengshui, Renqiu, Nangong, Bazhou, Dacheng,
Quzhou and Jinzhou and the central subsidence can be added up to 850mm.
The subsidence averages 2.79mm/a in Xuchang in Henan Province,
and about 57mmsubsidence in Puyang over 140 km2 in 1997.
Land subsidence 113mm in Kaifeng made the surface
building destroyed. The subsidence area summed up 8798.12km2,
of which there is 4080.48 km2 subsided over1000mm totally,
some subsidence centers just located at city proper. To 1998, the subsidence
center at city proper Tanggu, Hangu accumulated the most subsidence 2.81m, 3.09m and 2.84m respectively. The
Huabei plain subsidence is serious made up a part of. subsidence rate reduced
in evidence as a result of executive control subsidence measures by Tianjin
Government. For example, exploitation reduction was from 1×108m3/a in 1985 to
2435.26×104m3/a in
1998.correspondingly, and groundwater exploitation reduced form 27.4×104m3/a•km2 to 5.29×104 m3/a•km2(Fig.2).
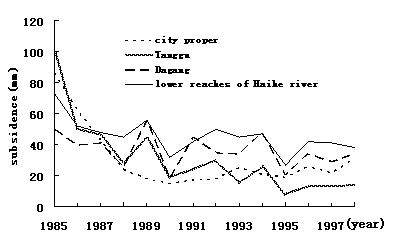
Fig.2 The subsidence curve of subsidence region in Tianjin
2.3 Geo-fractures
The geo-fractures
have taken place frequently since 1980s on the alluvial fan, depression, the
paleo-river course and exsisting river channel as a result of overexploitation
groundwater. The fractures lasted a few meters to 500m and even
longer. Some of them is over one thousand meters with the width about 2m at
maximum in Handan, Yongnian, Cheng’an, Daming, Nanhe, Zhaoxian, Xinle,
Zhengding, Gaocheng, Baoding, Renqiu, Suning, Bazhou, Zhuozhou, Wen’an and
Gu’an town in Hebei Province. Geo-fractures in Shandong province
mostly occurred in Zibo, Jining, Tai’an, Zaozhuang. They are from a few
meters to hundreds of meters with the depth over 10m. Geo-fractures may
bring great damages to industry, agriculture and even lives.
2.4 Land collapse
Land collapse is
mainly distributed in Hebei Province such as Tangshan city proper, JingXian in
Hengshui, Xushui and Zhuoxian, Zhaoxian in Baoding area, Wuji, Xinji and Luquan
in Shijiazhuang area, Yongnian in Handan area, Nanhe, Qinghe and Renqiu in
Xingtai. Land collapse in Xushui is of the most severity, its starting in 1974,
frequently developing during 1993 and 1999. About 200 houses were cracking in
EW direction. The land collapse is caused by groundwater pumping, rainstorm,
groundwater infiltrating creep, water releasing media compact and etc.
2.5 Seawater
intrusion
Seawater intrusion
is kind of environmental geology problem along the coastal area. The seawater
intrusion may cause high TDS, chloride in groundwater, water salted in the
well. Groundwater then is unfit for drinking. Overexploitation of groundwater
is the main reason to cause seawater intrusion. Seawater intrusion occurred in
the middle of 1970s in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain and intensified in 1980s in
Zaoyuan waterhead of Qinghuangdao in Hebei Province and
Shouguang-Weifang-Changyi area in Shandong Province
2.6 Soil
salinization
Soil salinization
is comparatively strong damage to crops. In recent years, the severe drought
has increased compumtion of groundwater for agriculture and industry, thus it
has caused groundwater level lowered and the waterlogging works with synthetic
measures reduced salt accumulation in soil. As the result, the saline area in
the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain has become smaller and the salinized area totals 30%
compared in 1980s. The dominant soil salinization appears along the coastal
area. In addition, it also appears at the inland wash of alluvium plain.
Prevention against salinization should be executed effectively according to its
cause and character combined with drought, waterlogging, alkali, salty. The
reasonable and efficacious irrigation-drainage system is also important.
Groundwater level should be kept lower and organic fertilizer for the farmland.
2.7 Groundwater
contamination
Groundwater contamination commonly takes place in two sides of rivers,
cities and the area around, mostly as point and line distribution but few as
area distribution in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. The shallow groundwater
contamination is comparatively serious. With exploitation period and amount
increase, the deep groundwater is contaminated at various degrees. The main
contaminants are total hardness, TDS, 3 types of nitrogen, sulfate, chloride,
iron and manganese, in which the total hardness and TDS are most serious beyond
standards. Contaminants mostly come form a large amount of sewage-farm, use of
more fertilizer and pesticide, waste water discharge from industry.
Contamination is influenced by human activities as well as hydrogeological
conditions. Therefore, groundwater contamination is taken as a line from the
mountainous area and the alluvial plain, the middle plain area and the coastal
area from light to heavy contamination. The mountainous area and the alluvial
plain belong to no or light contamination, the main contaminants nitrate,
nitrite. The moderate contamination main happen in the middle part of the
plain, the main contaminants total hardness, nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, TDS,
pH, hydroxybenzene, sulfate. The heavy contamination is in the coastal area,
the main contaminants nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, iron, manganese, fluoride and
iodide.
3 Countermeasures
and Advice to Groundwater Resource Protection
The Huang-Huai-Hai
Plain is the most severe area at environmental geology problems in China.
The social and economic sustainable development has been effected by
environmental geology problems. And the overexploitation of groundwater is the
direct cause, and water conservancy project, agriculture irrigation,
distribution of supply well and unreasonable industrial structure are factors
to effect environmental geology problems. Therefore, the measures are as
follows:
1) Scientific
management and programming should be strengthened on groundwater resources with
combination of exploitation and recovery. The reasonable planning should be executed
to control water level, irregular exploitation in order to stop ecological
environment from deteriorating continuously. According to environmental
capacity, the industrial structure should increase its efficiency for water
utilization;
2) Watersaving and
environmental law should be perfected. The solid waste cannot be dumped in the
groundwater vulnerable zone and wastewater discharge should restrictedly be
controlled. Pollution should be the first aim to control from pollution source;
3) Education
should be enlarged on water protect. Water resources should be careful of
economical use. The shallow groundwater is regarded as main exploitation layer
with combination of shallow and deep, salty and fresh water mixing use. The
principle should insist on the high quality water supply excellent using;
4) Research work
on resources renewable, environment repairable and groundwater exploitation
technology should be developed in advance and technology should be used to
increase the treatment of waste water and re-use it;
5) Groundwater environment monitoring network should be improved in the
municipal area and the industrial area to obtain first-hand data for protection
of groundwater environment and more research work..
References
[1] Chen Mengxiong,
“China Groundwater Resources and Environment”, Seismological Press, 2002.
[2] Chen Wanghe,
“Groundwater in Hebei province ” , Seismological Press, 1999.
[3] Gao Taizhong, Liu
Tongsheng, et al. “Environmental Problems of groundwater and continuously
development Countermeasure in the Ji-jing-jin plain”, minerals resource
·geological environment · economic management—The studys volume of 50
anniversary of the founding of Shijizhuang economy college,Geological Publishing House, 2003, P308-313.
[4] Xiao Guoqiang, Li
Fenglin, Liu Fengchuan et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Hebei[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Hebei, 2002.
[5] Zhu Zhongdao, Zhe
Xichun, Wang Jihua et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Henan[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Henani, 2002.
[6] Xie Zhenhu, Miao
Liwen, Chen Zhongrong et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Pekin[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Pekin, 2002.
[7] Xing Guifa, Wang
Lanhua, Lu Changjun et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Tientsin[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Tientsin, 2002.
[8] Liu Yanbo, Li
Yanguo, Duan Xiuming et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Shandong[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Shandon, 2002.
[9] Peng Yuhuai, Yang
Zhaojun, Wang Shaolong et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Anhui[R],
Bureau of Land and Resources of Anhui, 2002.
[10] Gu Aming, Zhu
Jinqi, Tao Yun et al, Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Jiangsu[R], Bureau
of Land and Resources of Jiangsu, 2002.




