Evolutional Rules of Regional Groundwater System
LANDFORMS EFFECT THE DISTRIBUTION AND CIRCULAR MODE ON GROUNDWATER IN SHIYANG RIVER BASIN
Gao Yexin1 ,Wang Guiling1 ,Liu Huatai2 ,Liu Zhiming1 ,Lin Wenjing1 ,Wang Jianzhong1
1 Institute of Hydrogeology and environmental geology, CAGS, Zhengding, Hebei, 050803,
2 The Environmental Science Research Centre of Xiamen
University, Xiamen,
361005,
Abstract: The paper discussed the relation between landform and groundwater. With the result that, the distribution of hydrogeology units and morphologic units are the same, because different morphologic units supply different distribution status and circular mode for groundwater. Mountainous and hills area are the replenishment headwater because their hole and cranny are space that groundwater exist. Alluvial fans are the location that groundwater reserves and circulates. Groundwater has different existence status in subsurface of plain because of different lithology, thickness, density and porosity in sediments. Frozen crust water mostly exists exceeding cold mountain area.
Keywords:
Shiyang River basin,
one of the highest among the 3 inland rivers, located in the eastern part of
Hexi Corridor in the middle
1 Geomorphic Feature
The geomorphic distribution is consisted of
mountain, hill, plain, lake and desert because of tectogenesis and climatic
change since Cenozonic era in Shiyang river basin. From south to north, the
landform is Qilian mountain in south, south basin that is made of Wuwei basin
and Yongchang Basin,
hill, north Basin that is made of Minchin
Basin and
Mountainous morphologic region: Firstly, Qilian mountain. Snow line is 3800m height. 1) The lithology is mainly made of metamorphic rock of lower Paleozoic Erathem and igneous rock of Caledonian in over snow line. The mountain is high 3000-4500m, steep and high, glacier erosion, intensity cryogenic weathering. The ravine is growth and distribute as branch. 2) The lithology is mainly made of metamorphic rock of Cambrian System and Ordovician System. The attitude is 2900-3300m, and attitude difference relatively is 500-800m. 3) Rock was intensively erosive by glide, which was made of metamorphic rock and limestone. Rainfall is much and forest is largely distribution here. The high and low terrace distributes among valleys because of glide erosive and mountains raise. Secondly, lithology is mainly made of red sandstone, schist, gneiss, migmatite and metamorphic rock in Mantoushan hill, Hongyashan hill, which is located in middle Shiyang river Basin, and North hill. The attitude is 1500-1700m, and attitude difference relatively is 160m. Island hill is the character. Surface bedrock was covered by crushing stones. Vegetation is sparse.
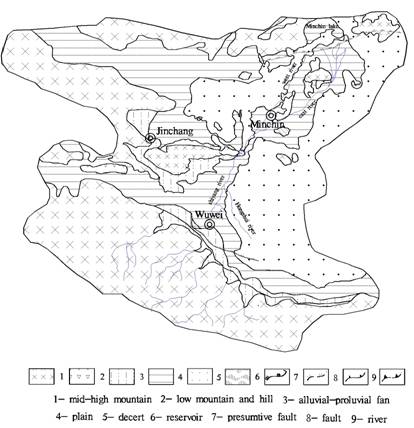
Fig.1 geomorphic feature of shiyang river basin
Lower mountain and hill geomorphic region: This zone is mainly made of three parts: The first part is fold and fault block lower hill in north side of Qilian. The lithology, covered by loess or clayey loam, is consisted of sedimentary of upper Psleozoic Group and Mesozoic Erathem. The attitude is 2400-3000m, and depth cut is 240-320m. The second part is low mountains and hills country in middle of Shiyang river basin. The lithology is consisted of red sandstone, schist, metamorphic rock and migmetite. The attitude is 1400-1500m. The three part is hills country in north of Shiyang river basin. The lithology is schist, marble and sandstone. The attitude is 1400-1600m.
Alluvial fan geomorphic region: The geomorphic region distribute foothill in north of Qilian. It is mainly made of sand gravel and cobble of Quaternary. The altitude is 1500-2000m, and gradient is 13-16‰. There are terraces in top alluvial fan. The cracked terrace is 3-10m height than riverbed. The alluvial fan is less in middle and north of Shiyang river basin than south.
Plain geomorphic region: In the south basin, lithology is sand gravel and cobble, covered by clayey loam that is 3-5m thickness in Quaternary. The attitude is 1300-1400m, and relief feature is flatness, and gradient is 3-5‰. There are some rivers in leading edge proluvial fan because of spring overflowing. The width of rivers is unequal, the best wide is 200m, and the deep is 3-7m. in the north basin, lithology is clayey loam, silt loam. The gradient is 2‰, and the attitude is 1200-1300m. Farming history has been over 1000 annual.
Terminal lake and desert geomorphic region : Relief types consist of locustrine plain and desert. Minchin lake, named “Zhuyeze” lake in history, is 50km from south to north, and 120km from east to west when it’s area is maximal, but the lake is gradually disappear before 1949 because water resource is absence. Now the lake region is farmland[5]. The surface relief of locustrine plain that located in northeast of Minchin basin is low and flat. There are wind erosion residual hills that are 1-5m high in surface relief because of aeolian erosion. There are many dunes in the earth’s surface. The desert consists of medium-fine sand, powder-fine sand of Holocene Series. Sand and herby dunes cover in the surface. Dune generally is 0.5-1.0m high. A kind of drought enduring plant grows in the edge of dunes.
2 Groundwater Feature
Burial condition of groundwater is very different and distribution on groundwater is very imbalance in mountain, hills, plain and desert area. Groundwater types and distribution range are controlled by landform as a whole (figure 2). Zonation is obvious from south to north. The distribution range and character of different groundwater types as follows (figure 3):
(1) Pore and fissured water in bedrock
Pore and fissured water in bedrock divided into four types: first, pore and fissured water in metamorphic rock and igneous rock distributes the medium-high mountain. atmospheric condensation is the recharge resource, and water quality is fresh water. Second, pore and fissure water in clastic rock distributes clastic rock stratum in low mountain, hill and structure residual region from upper Paleozoic Erathem to Cenozoic Erathem. Containing water medium is sandstone, sand gravel rock, granulite and conglomerate rock, and waterproof stratum is mudstone, sandy mudstone and shale. Groundwater generally is semi-confined and confined water. Groundwater recharge is nine tenths atmospheric condensation. When water-bearing stratum was cut by ravine, fracture and personal factors, groundwater overflows as spring and translate into surface runoff, fresh water.
(2) Pore water in friable rock
Pore water in friable rock distributes depression transition zone, and divide into two types according to existent condition: phreatic water in ravine that distributes the ravine of mountainous area, low mountains and foothill and pore water in plain terrain that distributes the deposit of Quaternary in basin. Aquifer is the stratum among gravel and pebble, medium-coarse sand and medium-fine sand of middle and upper Pleistocene Series. In south basin, aquifer is monolayer structure in alluvial and proluvial fan of foothill, water quality is fresh water. Leading edge of alluvial and proluvial fan is transition zone between phreatic water and confined water. Monolayer aquifer transits into twolayer in plain terrain. Phreatic water transits into semi-confined, confined water, and HCO3-Ca water transits gradually into SO4·HCO3-Mg·Ca water. In north basin, aquifer structure is multilayer in deposit of quaternary away from Qilian mountain. Fresh shallow seated water gradually transits into salt water, and salt water body gradually changes large from alluvial plain terrain to lacustrine plain.
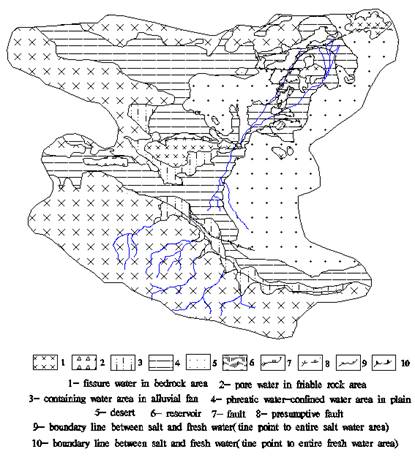
Fig.2 groundwater distribution in shiyang river basin
(3) Permafrost water
Permafrost water that is special type groundwater divided into permanence and temporarily permafrost water, and distributes in bedrock fissure and pore of loose layer of perennial frozen soil area in shiyang river basin. Permanence permafrost water is solid state. Temporarily permafrost water converts between groundwater and pore and fissure water because of the season change.
(4) Fissure and dissolved cavern water in carbonate rock
This type water distributes fissure and dissolved cavern in dolomitic limestone and shale of upper Simian System and marble of lower Proterozoic group. atmospheric condensation is the recharge resource. Distributing area is small.
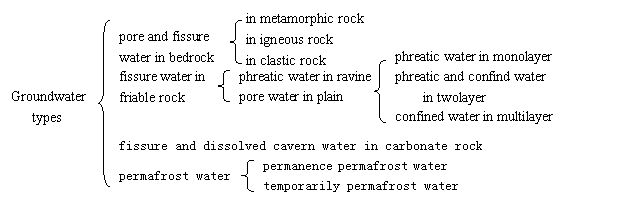
Fig.3 Groundwater types |
3 Morphologic Units Effect the Distribution and Circular Mode on Groundwater
Formation of groundwater is strictly controlled by stratum, lithology, structure, landform, climate and hydrology and so on. These factors are interrelation, mutual check. Groundwater formation is combined action result of many factors.
That morphologic units control action on groundwater mainly effects formation on groundwater in plain of foothill. Mountains and hills are positive topography, and plain of foothills are negative topography in terms of shiyang river basin. So, mountainous and hills area are the replenishment headwater, and plain is formation and runoff area of groundwater.
3.1 The relation between morphologic units and groundwater types
The result shows by comparing figure1 with figure2 different type groundwater to distribute as band from south to north. The boundary line between different type groundwater and morphologic units is identical. The identical relation shows that landform controls action on groundwater. Different morphologic units control groundwater types (table1). For example, single structure phreatic water grade into multi-structure confined water in alluvial flat from foothill to the central section of basin. Groundwater types are mainly multilayer confined water in lacustrine plain, and water quality also underlying rules changes. Phreastic water is salt water and deep confined water is fresh water. Some semi-confined and confined water is salt water in middle part of lake area.
Tab.1 Corresponding relation between morphologic units and groundwater types
|
morphologic units |
landform subunits |
groundwater types |
|
medium-high mountain |
glacier in medium-high mountain |
permafrost water |
|
medium-high mountain |
no glacier |
pore and fissure water in bedrock |
|
lower mountain and hill |
pore and fissure water in clastic rock | |
|
alluvial-proluvial fan |
unconfined water, unconfined-confined water | |
|
alluvial flat |
multilayer structure, deep buried confined water |
3.2 Morphologic units affect circular mode on groundwater
Groundwater circle mode is different in each landform zone that rang from south to north in shiyang river basin. According to different hydrogeology condition, shiyang river basin is divided into eight hydrogeology units: recharge zone, water-resisting zone in piedmont hill, level runoff zone, overflowing zone, vertical alternative zone, water-resisting zone in lower mountain and hills, evaporation from phreatic water zone and water-resisting in north mountain(figure 4). So, it is one-to-one correspondence between morphologic units and hydrogeology units (table 2). The medium-high mountain areas are recharge headwater in whole basin. The recharge mode mainly is atmospheric condensation, glacier melting water, river infiltration and so on. There is abundance precipitation in this area. Part of water directly replenish river, and part of water replenish fissure water of bedrock and interstratified water by infiltration. Water resource in mountain area recharges plain by river.
Clastic rock that makes up piedmont and hill in Qilian mountain forms the first water-resisting zone. Sand rock in hongyashan hill is the second water-resisting zone. Groundwater has not directly hydraulic connection in hongyashan hill between south and north basin, other person have approved this point by researching. North hills formed the third water-resisting zone. Minchin lake formed here because Shiyang river can’t flow to north again.
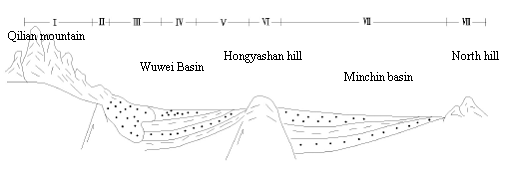
Ⅰ—recharge zone; Ⅱ—water-resisting zone in piedmont hill; Ⅲ—level runoff zone; Ⅳ—overflowing zone;
Ⅴ—vertical alternative zone; Ⅵ—water-resisting zone in lower mountain and hills; Ⅶ—evaporation from phreatic water zone; Ⅷ—water-resisting zone in lower mountain
Fig.4 Hydrogeologic cross section in the Shiyang River basin
Level runoff zone that belong to alluvial fan zone in landform types is that surface water intensely infiltrate zone, and is important recharge area. The thickness of aquifer in alluvial fan is large, and transmissivity is good. The particle that make up of aquifer is coarse. Drainage mode is manual exploitation and runoff down the river in this area.
Tab.2 Relation between morphologic units and hydrogeology units
|
number |
Morphologic units |
Landform subunits |
Hydrogeological units |
|
Ⅰ |
medium-high mountain |
medium-high mountain |
replenishment zone |
|
Ⅱ |
piedmont and hills |
piedmont and hills |
water-resisting zone |
|
Ⅲ |
alluvial fan |
body |
level runoff zone |
|
Ⅳ |
edge |
overflow zone | |
|
Ⅴ |
fine soil plain |
vertical alternative zone | |
|
Ⅵ |
hills |
water-resisting zone | |
|
Ⅶ |
alluvial plain |
evaporation from phreatic water zone | |
|
Ⅷ |
hills in north |
water-resisting zone |
Overflowing zone located in the edge of alluvial fan. the particle of deposit is fine. Water-resisting ability is enhancing because clay layer appear. Thus, the water table rise to overflow the earth′s surface by spring because groundwater flowing is slow. Groundwater transits surface water in this area. Recharge resource of groundwater is level runoff zone.
Vertical alternative zone locates in alluvial flat in south basin. Lithology that is bad permeability consists of fine sand, silt and clay in alluvial plain. Evaporation of groundwater is intense in this area. Vertical runoff of groundwater is primary way, and level runoff is poor than vertical runoff. Groundwater is only 1-3m depth. Drainge way is evaporation and manual exploitation.
Evaporation from phreatic water zone locates in alluvial plain in north basin. Recharge way of groundwater is infiltration of surface water, and evaporation from phreatic water is the primary drainage way because of single recharge resource and intense evaporation in this area. Degree of mineralization of shallow groundwater is higher than deep in lacustrine plain because evaporation capacity is great large than recharge capacity.
3.3 Morphologic units can equalize groundwater
Morphologic units have an equalization effect to groundwater. For example,river recharge groundwater in level runoff zone, and it forms spring when groundwater overflows the earth′s surface. Spring recharges surface water in the edge of alluvial fan,and surface water recharge river again by infiltration. So, we say that alluvial fan has a dynamic reservoir role. It is important that alluvial fan maintains quantity of water source in shiyang river basin.
4 Conclusion
Endogenetic and exogenetic force of geology engendered various topographic form. For example, loosing matter of the earth′s surface is migrated and deposited under fluviation and weathering condition. Because hydrodynamic condition is different, the coarse the particle of sediment is, the near sediment is from source area, and the fine, the far. This is the reason that physical makeup and structure that lead to hydrogeological water-bearing structure of different productive aquifer is different from mountain to plain.
Morphologic units take on obvious zonation character because regional tectonics controls the structure and basic configuration of morphologic units in shiyang river basin. Morphologic units that are existent space of groundwater control distribution and circular mode on groundwater. Different lithology that makes up morphologic units composed of different aquifer hydrogeological units.
As mentioned above, lithology that make up of landform is basic, structure that controls landform is primary factor, and landform combined lithology with structure.
So, different morphologic units formed a series of unequal scale water-bearing structure. This is the reason that landform controls groundwater.
Reference:
[1] Shi J A, Wang Q, Chen G J, et al. Isotopic geochemistry of the groundwater system in arid and semiarid areas and its significance: a case study in Shiyang River Catchment, Gansu Province, northwest China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2001,40(4/5):557~565
[2] Zhang Dianfa,L Fengquan, B Jiamin. Eco~environmental effects of the Qinghai~Tibet plateau up lift during the Quanternary in China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000,39(12):1352~1358.
[3] Liu Zhiguang, Pan Baotian, Wu Guangjian, et al. Initial research of summer monsoon change at desert marginal zone in the northwest of China since the last interglacial [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2000, 20(4): 44-49.
[4] Guo Xiaoyin, Chen Fahu et al. A study on modeling the terminal lake of shiyang river drainage basin under the natural conditions. Journal of natural resources[J]. 1999, 14(4):385~388
[5] Feng Shengwu. The evolution of the drainage system of the Minchin oasis[J]. ACTA geographica sinica. 1963,29(3):241~249




