Evolutional Rules of Regional Groundwater System
THE HYDROCHEMICAL CHARACTERA OF MULTI- AQUIFERS SYSTEM IN QIONGBEI AREA OF HAINAN
Guo Chunqing
Abstract: By using the methods of hydrochemistry, isotope hydrology and fractal dimension theory, we have a comperhensive hydrochemical research of multi-aquifers system in Qiongbei Area of Hai Nan. The results show that the groundwater power relation is extremely close amount the multi-aquifers; the hydrochemical types are complex and changeable; the content of Cl- increases as time growing ,but still in low state,and it’s hard to estimate whether there is seawater invasion or not. In partial areas the content of Cl- raises obviously showing the water has been salted and the monitoring of water quality should be strengthened in order to prevent and control the seawater invading.
Keywords: Qiongbei area,the system of multi-aquifers,hydrochemistry
1 The Synthesis Elaborates
The Hai Kou city locates the south wing of Leiqiong artesian basin (Qiongbei artesian basin) in which the groundwater resources is rich.In recent years as the unban’s economic development,the groundwater’s level in every aquifer drops year by year as a result of massively mined.The funnel area expends unceasingly and even have the tendency to the sea.The problem of preventing from the seawater invasion and protecting groundwater resources is important day by day .In view of the problem above,we has done some works in this area and yielded some results provide some scientific evidences for formulating policy of reasonable development groundwater resources and preventing from the seawater invasion.
This research area (Qiong Bei artesian basin) mainly includes Haikou city and neighboring Qiongshan country. The Dongzhai Harbor is in the east, the Shizi road in the south, the Lingao country in the western, and the the north boundary is the Qiongzhou channel.In order to keep the hydrogeological unit’s completeness, the research area expand to the eastern part of Qiongbei artesian basin (Fig. 1).
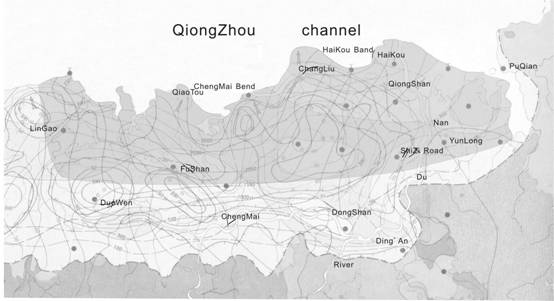
Fig. 1 The Position Figure of QiongBei Research Area
1.1Topography and landform
The terrain in research area is low and flat, and the south’s is higher than the north’s in totality. The south area the terrain is relatively high is of volcanic rock formed by the 1~3 level plateau, and the indicated altitude is from 20 to 100m. The north area mainly distributing in the coastal area is coast plain formed by 1~3 level terrace being marine facies, and the indicated altitude is from 1 to 28 m.
1.2Meteorology and Hydrology
The research area is tropics monsoon climate. It’s hot in noon and cool in night. All year long there does not have the frost and have more fog and arid in winter and spring and more thunderstorms and typhoon in summer and fall. The surface river system is mainly the Nandujiang River originated from Nanfeng Mountain in Baisha County and flowing though Chanzhou, Chengmai and An’ding to the sea from Haikou. Furthermore, there are Songtao, Yonzhuang reservoirs and Wuyuan, Haidian Rivers.
1.3 Geological survey
The research area locates the plateau of north Hainan Island belongs to south wing of Qiongbei nascent fault basin which the land area is about 4300 km2 and Leiqiong concavity. From tertiary epoch, the basin has been deposited a stratum of consolidated-half consolidated loose and clay. In Miocene Epoch and Holocene Epoch there’re multi- times volcanic eruption and large surface is covered by volcanic basalt and tuff. The basin’s basis and edge is red rock of Cretaceous system, partialy be metamorphic rock of Cambriam system and magmatic rock of Mesozoic Era.
In the artesian basin there’re many growing intensely fractured structures mainly dividing into four groups of east-west, south-north, and north-west and north-east directins (Fig. 2)
Fig. 2 The regional geological structure map
2 Structure and Hydrochemical Characters of Multi-aquifers System
In research area the multi-aquifers system divides into phreatic aquifers and confined aquifers. The phreatic aquifers include loose pore aquifer of the Quaternary Period and phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock; the confined aquifers include 7 aquifers from above to below. As to the loose pore of the Quaternary Period aquifer’s thin depth and the 5~7 confined aquifers’ mineral middle-low thermometric water we hasn’t done studies in those area. The impermeable layer is instable and there’s regularly water power conection between the third and fourth confined aquifers so that let them to be combined one –the third confined aquifer. In all the multi-aquifers system we studied involve the phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock and the first, the second and the third confined aquifers.
2.1 The phreatic practured aquifer of volcanic rock
2.1.1 Structure
The depth of phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock is of between 1 and 14 m and spread from east to west. The phreatic water is stored in volcanic rock of Holocene Epoch and Pliocene Epoch. The aquifer lithologicals are vesicle basalt, volcanic clast, and tuff and so on. The medium type is mainly pore space. The rainfall infiltration is very good and the infiltration rate could be from 0.25 to 0.80.
2.1.2 Character of water cycle
The groundwater is supplied by rainfall infiltration mainly and seasonal surface river secondly. The runoff types are vertical and horizontal directions. In vertical direction the phreatic water outpasses to the underlying aquifer by the way of piont,line, surface and so on; In horizontal direction the groundwater flows radiusly to all around taking volcano groups as the center. The elimination goes by the way of fountain or underflowing (Figure 3).
2.1.3 Hydrochemical characters
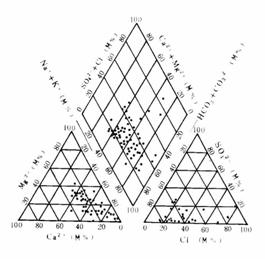
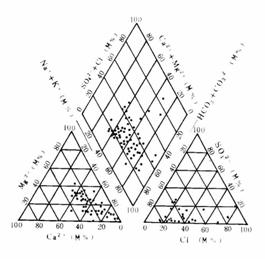
The hydrochemical types are more and complex mainly about HCO3—Mg·Ca·Na、HCO3—Mg·Ca and HCO3—Na·Ca. The groundwater most is of silicate low-mineralization. The content of TDS, total hardness, and acidity are low but the fusile silica and co2 partial pressure are higher; the mineral in water such as calcite, dolomite, and gypsum are unsaturated. The water in the plant from Haikou flour mill to Yusha is little-salt and the hydrochemical type is Cl—Ca·Mg. The content of Cl-, TDS (total dissoved solids) and total hardness is little higher but lower as the increasing of depth. The hydrochemical type changes into Cl·HCO3—Na·Ca and it shows the mixture between groundwater and salt water (Fig.4).
2.2 The pore confined aquifers
2.2.1 Structure
(1) The First Pore Confined Aquifer
The depth of this aquifer is of between 2 and 50 m and spread from east to west nearly. The confined water is stored in the fourth Segment Haikou Group of Policene Series. The aquifer lithological is offwhite and russet conch fragment rock. The medium type is mainly and conch space. The rainfall infiltration is good but in partial areas.
(2) The second pore confined aquifer
The depth of this aquifer is stable from 30 to 50 m. the tendency of buried line becomes deep from east-south to north-west. The confined water is stored in the second Segment Haikou Group of Policene Series. The aquifer lithological is brown and cuit-red color conch boulder but loose fragment rock containing conch in partial areas. The in Haikou, Rongshan and Macun is thick and loose and is of in the downstream region of groundwater’s runoff, so the water yield property is very good and is bad in Yunlong,Shizi Road and An’ren because the aquife thin and the rock structure is dense.
(3) The third pore confined aquifer
The depth of this aquifer is unstable from 7 to 10 m. The layer distributes the entire area except Yunlong distrct. The tendency of buried line becomes deep from east-south to west-north. The confined water is stored in Changliu Group of Policene Series. The aquifer lithological is offwhite and green middle coarse sand、coarse with boulder、middle fine sand、and powder. The medium type is mainly pore and the water yield property is good.
2.2.2 Character of water cycle
The groundwater is supplied mainly by the way of vertical infiltration from the same sources. The aquifers in turn accept water from the phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock by many outpassed ways and the water exchanges due to pressure head between neighboring aquifers. Many partial areas accept water from rainfall or Nandu River directly. The aquifers also accept partly water from side direction. The groundwater flows radiusly to all around taking volcano groups as the center. Dongzhai Harbor, Nandu River of above The Iorn Bridge and Qiongzhou channel is the natural excretion area, the centralism mining area of Haikou is the largest artificial excretion area (Fig. 3).
|
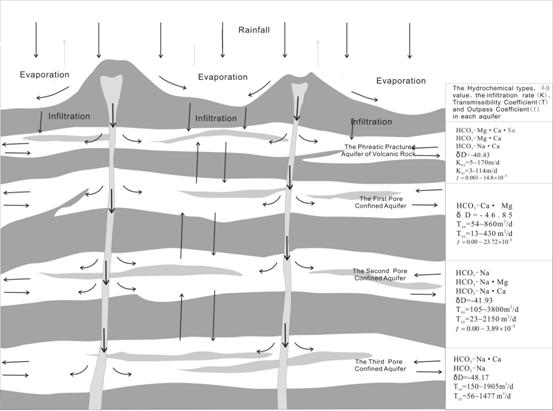
What’s more, the natural flow field has changed because of the larger artificial mining of water from the second confined aquifer. The second confined aquifer groundwater is supplied by the first and the third confined aquifers though the artificial mixed mining hole and dormer.
2.2.3 Hydrochemical characters
(1) The First Pore Confined Aquifer
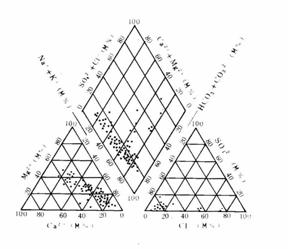
The hydrochemical types are mainly HCO3—Ca·Mg and next are HCO3—Na·Ca and HCO3—Na. In less area it’s HCO3·Cl—Ca·Mg. The groundwater most is of silicate low-mineralization.The content of TDS, total hardness, and acidity is higher than the aquifer above and the fusile silica and co2 partial pressure are lower. The mineral of calcite, dolomite in water are saturated and gypsum is unsaturated. Less holes’ (M64) content of Cl-is five times high than initial state estimating because of the shallow salt water’s effect (Fig. 4).
(2) The Second Confined Aquifer
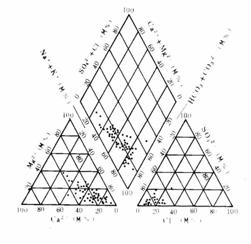
The hydrochemical types are mainly HCO3—Na, HCO3—Na·Mgand HCO3—Na·Ca and in partial areas are Cl·HCO3—Na and SO4·Cl—Ca·Na. The groundwater most is also of silicate low-mineralization. The content of TDS, total hardness, and acidity are higher than the first confined aquifer and the fusile silica and co2 partial pressure is equivalent. The mineral of calcite, dolomite in water are saturated and the extent is little higher than the first confined aquifer. The gypsum is unsaturated (Fig. 4).
(3) The Third Confined Aquifer
The hydrochemical types are mainly HCO3—Na·Ca and HCO3—Na next. The most is also of silicate low-mineralization. The content of TDS and total hardness are higher than the second confined aquifer and the acidity, fusile silica and co2 partial pressure is equivalent. The mineral of calcite, dolomite in water are saturated and the extent is little higher than the second confined aquifer. The gypsum is also unsaturated (Fig. 4).
|
|  |
|
The Hydrochemical Element Three-wire Map of The Phreatic Practured Aquifer of Volcanic Rock |
The Hydrochemical Element Three-wireMap of The First Pore Confined Aquifer |
|
|
|
|
The Hydrochemical Element Three-wireMap of The Second Pore Confined Aquifer |
The Hydrochemical Element Three-wireMap of The Third Pore Confined Aquifer |
Fig.4 The Hydrochemical Element Three-wireMap of Each Groundwater Aquifer
3 Isotopic Characters of Groundwater
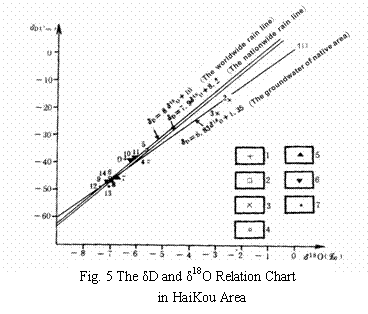
From the graph of relation between δD and δ18O (Fig. 5) we can see the most δD and δ18O values of groundwater sample points are near from the nationwide and worldwide rain line showing the area is evaporating in a balancing situation. The value relation between δD and δ18O is linear relation basically and the linear equation is:
|
δD=6.83δ18O+1.35(r=0.9339)
From the linear equation we can see the groundwater power relation is extremely close amount the multi-aquifers and the supply is the same resource.
4 Fractal Dimension Distinguish of Cl- Limiting Surface
The main exploited layer is the second confined aquifer, so we has done fractal dimension distinguish of Cl- limiting surface in it only for judging seawater invading.
First take the Cl- concentration MV of north boundary blast holes of the second confined aquifer from 1991 to 1993, then mesh the geographical coordinate (longitude: 19 420 000~19 450 000; latitude: 2 200 000~2 220 000) to 30*20 and take Cl- concentration interpolat to mesh points by the Kriging method.finally get the particular fractal dimension graph by the R/S analysis of fractal dimension theory (Fig. 6).
Form Fig.6 we can see:
(1)The cl- fractal dimension outliers are similar from 2.04 to 2.07 show the cl- concentration change unobvious in space and we can’t estimate whether there is seawater invasion or not.
(2)In the area near from YanFeng of DongZhai Band and the east-north, west of HaiKou city, the cl- outlier is higher shows that the cl- concentration is abnormal in those areas.
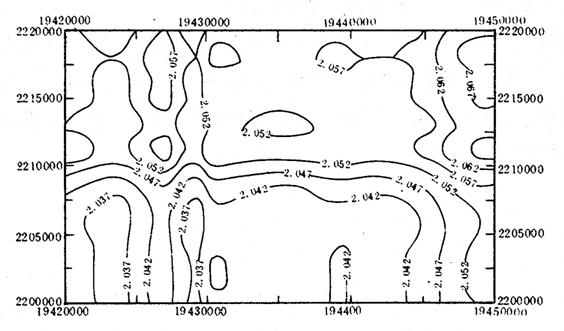
Fig. 6 The Fractal Dimension Contour
Diagram of Cl-
4.1 Fundament of R/S analysis method
Considering time order {ξ (t), t=1, 2…} and definite average order
![]()
Accumulated dispersion
![]()
Range
![]()
Square root of the variance
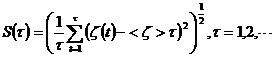
So
![]()
H-Hurst fingers
4.2 Treatment of two-dimension hydrochemical data matrix
(1) Cl- concentration values of blast holes are allocated to a two-dimension matrix having n lines and m rows by Krige, and extract ζ ranges and squares root of the variance taking each line and row as a apace matrix, then create R/S and lnR/S-lnζ graph. The points are near a line, and the line’s slope is H being used to calculate line fractal dimension ai (i=1, 2… n) and row fractal dimension bj (j=1, 2… m).
(2) Get total fractal dimension (line direction and row direction) and definite average order in line direction
![]()
Definite accumulated dispersion in line direction
![]()
Square root of the variance
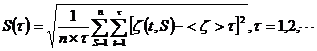
The other parameters are the same to those above, and we can get the total fractal dimension A and B in line and row direction.
(3) Create fractal dimension matrix and the elements are:
dij=(aij,bij) (i=1,2,…,n;j=1,2,…,m)
(4) Get the distance fractal dimension vector in each union
![]()
C
reat contour diagram in view of ![]() and it shows the exception of
total fractal dimension
background to every union, we call the diagram particular fractal dimension graph.
and it shows the exception of
total fractal dimension
background to every union, we call the diagram particular fractal dimension graph.
5 The Conclusions
(1) The concentration of main chemical compositions containing TDS, total hardness and normal ions in every aquifer’s water increase from supplying areas to runoff and excretion area in horizontal area and also increase from above to below in vertical cut plan.
(2) The average value of Cl- of every aquifer’s water increases obviously as time growing especially in the second and first confined aquifers, but the content still is low. The content of Cl- in the phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock is higher than the confined aquifers below (Fig. 7).
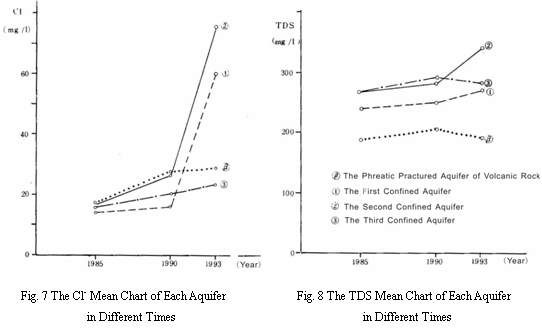
(3) The average value of TDS in each aquifer increases as time growing except decrease in the phreatic fractured aquifer of volcanic rock and the third confined aquifer from1991 to 1993(Fig. 8).
(4) The content of SO42- decreases as time growing and the others such as PH,HB,Ca+ ,Mg+ ,Na++K+ and HCO3- don’t change obviously.
(5)In the area the outlier change unobvious, so it’s hard to estimate whether there is seawater invasion or not.
References:
[1] Guochunqing,chenanhe ,the theory and method of model exploration of groundwater system, the teachers university of GuangXi publishing firm
[2] Xue Yu Qun, The Salt-fresh Water Surface Migration Research of Seawater Invading,NanJing, the university of NanJing publishing firm, 1997.
[3] Shen Zhao Li, The Base of Hydrochemisty, Beijing, The Geological Publishing Firm, 1993.
[4] Sun Na Zheng, The Groundwater Pollution-mathematical Simulation and Methods, The Geological Publishing Firm, 1989.
[5] The Geological Mineral Headquarters and Geological Environmental Administrative Department, Water Resources and Geological Environment Assessment in Major Countries of Coastland, (The Internal Publishing Firm), 1990.
[6] Zeng Zhao Xuan, The Physical Geography of Hainan, Beijing, The Scientific Publishing Firm,1989
[7] Wang Da Chun, The Base of Hydrogeology, Beijing, The Geological Publishing Firm, 1995
[8] Wang Kai Xiong, The Hydrochemistry, The Chamical and Industrial Publishing Firm, 2001
[9] Xiao Ai Lan, General Chemisty and Hydrochemistry, The China Water Conservancy and Hydroelectricity Publishing Firm,1993.
[10] Shen Xian Chen, Natural Hydrochemistry, The China Environmental Science Publishing Firm, 1994.
[11]Song Xing Yuan, The Analysis and Prediction of Water Environment, The Wuhan University of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectricity Publishing Firm, 2000