Achievements
SLIP-RATE OF THE BENGCO DEXTRAL-SLIP FAULTAND FRACTURES FROM THE Ms 8.0 BENGCO EARTHQUAKE
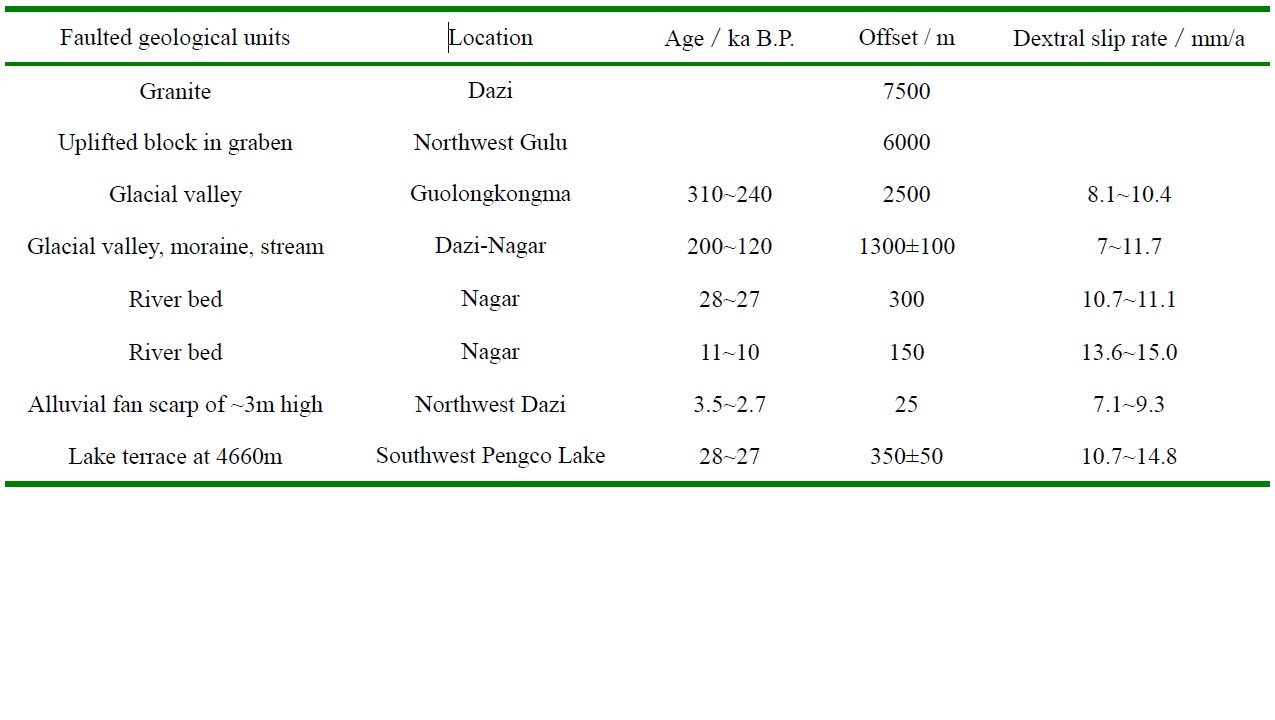
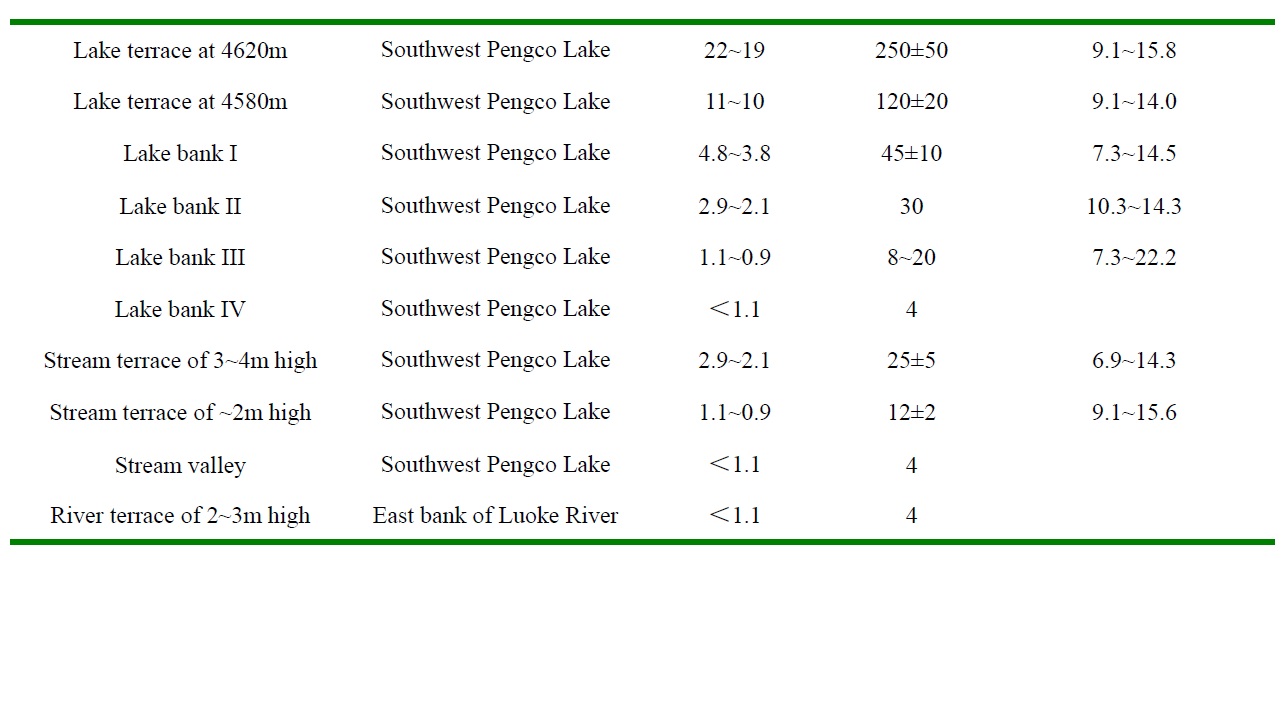
The northwest-trending Bengco active fault forms the middle segment of the Karakorum-Jiali fault system, which is dominated by dextral strike-slip in the southern Tibetan Plateau (Armijio et al., 1989). It is an important regional seismic zone and where the Ms 8.0 Bengco earthquake occurred in 1951 and the site of several intense earthquakes in Holocene (Fig.8). The Bengco active fault is 100~120km long. It extends from east of Bengco Lake westward to Jiangco Lake and includes Lana-Songuo, Cuodaru-Dasa and Longqin-Guolonkonma segments. Bedrock, ridges, streams, glacial valleys and lake terraces were offset dextrally along the Bengco active fault at a rate of 7-16mm/a in Late Pleistocene-Holocene (Table 3). Seismic fractures, pressure ridges, sag ponds and pull-apart basins formed along Bengco active fault during the Ms 8.0 Bengco earthquake and ~8m of dextral slip occurred near the epicenter of the earthquake. The average strike-slip-rate and return time of Ms 8.0 earthquakes in Late-Pleistocene-Holocene are estimated as 11.5±4.5mm/a and 900±500a respectively for the Bengco active fault (Wu et al., 2005).
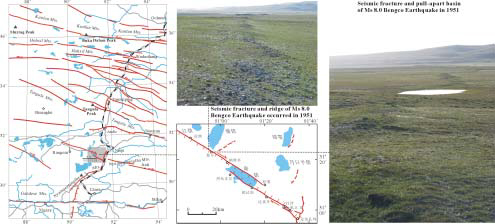
Fig.8 Map of Bengco dextral slip fault and seismic fractures of Ms 8.0 Bengco Earthquake occurred in 1951
Table 3 Slip-rateS of Bengco dextral slip fault for various time intervals