Groundwater Quality Safety and Contamination Recovery
ANALYSIS OF THE REASON FOR HIGH MINERALIZATION CRETACEOUS GROUNDWATERIN BAIYU MOUNTAIN AREA
Li Yunfeng1,Feng
Jianguo1,Wang Jiangxia1 ,Wu
Yaoguo2,Qu Hui1,Hou Guangcai3,4
1. School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang'an
University, 126 Yanta South Road, Xi'an, 710054, China, E-mail:
lyfphd@163.com, Tel:
+86-29-82339960
2.
3. Xi´an Institutes of Geology and Mineral Resources,
4. Jilin University,
Ximinzhu Street 6,Changchun,Jilin Province, 130026, China, E-mail:
suxiaosi@jlu.edu.cn, Tel: +86-431-8502595
Abstract:The water resource in BaiYu mountain area in
Keywords BaiYu Mountain,cretaceous groundwater,High Mineralization,lithofacies and
paleogeography,Tian Huan syncline
1 The Exceeding Lack of Water in
Erdos basin locates in the east of the northwest region in our
country, go beyond five provinces (municipalities):
The present physiognomy of
With the characteristics above-mentioned, the lack of water in the
BaiYu area is more serious in
The content discussed in this paper doesn’t involve the problem of
water quantity in the BaiYu mountain area, but the present condition of high
mineralization and poor quality groundwater and its causation.
2 The Analysis of the Present Condition of Complex Quality of
Cretaceous Groundwater in
Group stratum of Lower Cretaceous is land facies fragmental rock
formation,Its lithology is complex,
composed of sandstone, siltstone and mud stone, which frequently alternate and
repetitively fold as multiplayer lamellar structure. It is a multilayer structure
groundwater system. According to the deposit gyration and the property of
aquiferous medium, this groundwater system, from top to bottom, can be divided
into Luohandong water-bearing rock group,
Analysis of the present condition of water quality in
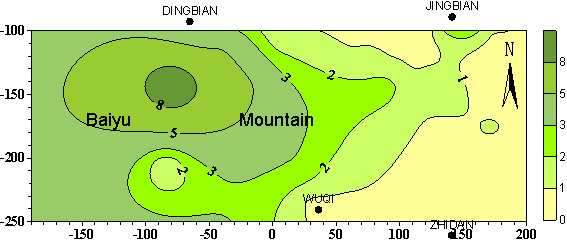
From all of the above, we know, the TDS of the cretaceous
groundwater in BaiYu mountain area is the highest, and the water quality is the
most complex. Influenced by the high TDS and the complex water quality, the TDS
of the base flow of the river in BaiYu mountain area is more than
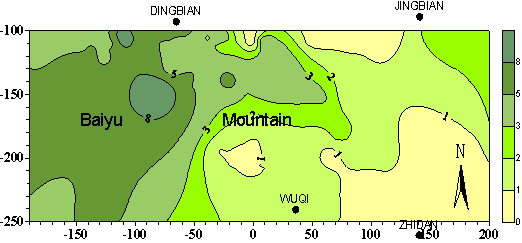
3 The Analysis of the Reason For the Complex Quality of Cretaceous
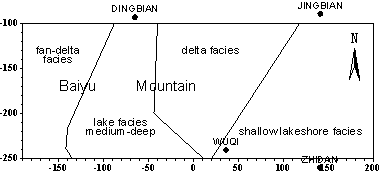
Groundwater in The reason for such high TDS and such complex water quality of the cretaceous groundwater in BaiYu mountain area is not single. It relates to the location of special geologic structure and special lithofacies and paleogeography condition. 3.1 Influenced by the lithofacies and paleogeography condition of cretaceous in BaiYu mountain area Regarding the whole Erdos Basin, the sediment environment of Lower Cretaceous stratum includes six sedimentary facies:alluvial or pluvial fan facies、braided fluviatile facies、meandering stream facies、lake facies and desert facies. The lake facies can be further divided into shore lake and shallow lake sub facies、hypabyssal lake subfacies。The lithofacies and paleogeography of Luo Rive in BaiYu mountain area is showed in figure 3. From figure 3, we can know that Luohe group in BaiYu mountain area includes three deposition environments:lake and fluviatile facies、lake and fluviatile mutual facies、wind facies;The lithofacies and paleogeography of Huan Rive group in BaiYu mountain area is showed in figure 4. Figure 4 indicates that Huanhe group includes four deposition environment: fanlike delta facies,delta facies,hypabyssal lake subfacies,shore lake and shallow lake facies. Whether the lake and fluviatile facies、lake and fluviatile mutual facies of Luohe group,or the hypabyssal lake subfacies、shore lake and shallow lake facies of Huanhe group,it presented as low-lying landform at that time, and it connected the north and south foot of BaiYu mountain, spreading across the BaiYu mountain. In addition,The lithofacies and paleogeography of Luohandong group in the west of BaiYu mountain is a more longer and narrower lake and fluviatile facies low-lying zone, connecting the north and south. The lake and fluviatile facies low-lying zone of the lithofacies and paleogeography of three water-bearing rock groups of Bao-An group, on the whole, superposes with the axis of Tian Huan syncline. And this makes the water in each aquifer in the east and west drain to the lake and fluviatile facies low-lying zone of the three water-bearing rock groups of Bao-An group, forming the drainage zone. As a result, the TDS of the groundwater is high and the water quality is poor in this drainage zone. |
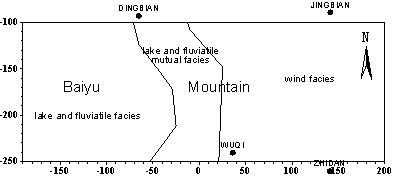
|
3.2 Influenced by the main geologic structure--Tian Huan syncline
in the basin
The depth of Tian Huan syncline can reach to lower Paleozoic. But
its west wing becomes more narrow and steep when reaches the lower Paleozoic.
The main part of Tian Huan syncline is the syncline sructure of cretaceous,
which is dissymmetrical, with broad east wing and narrow west wing. The axis of
the syncline vertically shifts to east gradually from bottom to top. The most
thickness of cretaceous deposit, which can reach 800
The Bao An group of
lower Cretaceous composing the syncline formation is land facies fragmental
rock formation,Its lithology is complex,
composed of sandstone, siltstone and mud stone,
which frequently alternate and repetitively fold as multilayer lamellar
structure. This iterative overlay multilayer lamellar geologic structure
determine that the groundwater aquifer system has the character of multilayer、artesian aquifer and the relative closing layer, The groundwater
in the aquifer of the two wings of syncline flows horizontally, hardly
vertically leakage. Therefore, the groundwater at the axis of Tian Huan
syncline comes far from the two wing of the syncline, continually dissolving
the rocks in the way continually. The content of the dissolvable salt in the
stratums of lake and fluviatile facies、shallow lake facies、deep lake facies is high, the mineralization of the far coming
water cannot but high. Analyzed from the regulation of horizontally zoning,the more down to the lower course of underground runoff,the more
nearer the zone of high TDS,and the more complex the groundwater quality is.
3.3 Influenced by the unfree flow condition of the water-bearing
rock group
The maximum thickness of the cretaceous deposition can reached to
800
As it related above, the groundwater in the aquifer of the two
wings of syncline flows horizontally, hardly vertically leakage. When the
groundwater arrives at the axis of the syncline, one small part flows
horizontally along the axis of the syncline, another small part vertically
flows to the up floor.
However, these two types of stream are both unfree. The former,
flowing horizontally along the axis of the syncline, is influenced by the more
downstream flow from the two wings of the syncline, jamming and robbing the
passage. And this makes such a small quantity of the passed water in the
upstream. While the vertical current to the up floor travels through the
Cretaceous system which composed of sandstone, siltstone and mud stone and which frequently alternate and repetitively fold as multilayer
lamellar structure, moreover with the Cainozoic group above, hundreds of
meters. As a result, the travel is very difficult, making the groundwater high
TDS and complex quality.
4 Conclusions
From the study of this paper, the following conclusions can be
gained:
1. Baiyu mountain area is exceedingly short of water, not only in
the quantity, but also more lack of high quality water that can be drunk and
irrigation..
2. Baiyu mountain area is the typical “bitter water region”. The
TDS of the groundwater in the Bao-An group of lower Cretaceous is more than
3. One reason of the high TDS and complex water quality of
cretaceous groundwater in BaiYu mountain area is that it is influenced by the
lithofacies and paleogeography.
4. The second is the special position of geologic structure it
locates, that is, it is influenced by the main geologic structure—Tian Huan
syncline.
5. The third is that, it is influenced by the unfree flow
condition of the cretaceous water-bearing rock group
References
[1] Shen
Zaoli Hydrogeology, science press, 1985,
[2] M.
A. Habermehl,The
Great Artesian
[3] G..Weinberger
E.Rosnthal Reconstruction of natural groundwater flow paths in the multiple
aquifer system of the northern Negev (
[4] Li
Yunfeng,Xu
Zhonghua,Wang
Jiangxia,Wu
Yaoguo,Hou
Guangcai Guidelines to locate and protect high-quality groundwater in Baiyu
Mountain area of China, Environmental Geology, Volume 47, Number 5, March 2005,
Pages: 647 – 652