Evolutional Rules of Regional Groundwater System
ANALYSIS ON THE WATER RESOURCES SYSTEM OF LAKE TAIHU BASIN AND CIRCULAR ECONOMY
Wang Dong1, Shi Yunliang2,Wu Jichun1, Gong Zheng3
1. Dept. of Hydrosciences, Dept. of Earth Sciences, Nanjing Univ., Nanjing, 210093, China, 86-25-83595591, wangdongml@hotmail.com
2. College
of Geography and Marine Sciences, Nanjing Univ.,
Nanjing, 210093,
3. Taihu Basin Authority of Ministry of Water Resources, Shanghai, 200434,
Abstract:Water resources possess both
social attribute and natural attribute. water resources system is a complicated
large system, which contains regional background, as well as specific
framework, function and dynamic balance. The evaluation of the water resources
system needs the measurement according to both water resources carrying
capacity and water environment carrying capacity, and the supervision with the
viewpoint of sustainable development. The water resources system of
Keywords: water resources system, circular economy,
water resources carrying capacity, water environment carrying capacity,
1 Introduction
Lake Taihu basin is located at the south end of the
Changjiang River Delta, bordering the Changjiang
River on its north side, facing the Hangzhou Bay
to the south, with mountain.Tianmu immediately to its west and East China Sea to its east.
2 Basic Concept of Water Resources System
2.1 Water resources and water resources system
According to the study both in and out of China, water resources can be defined as the renewable part of water body, which is adequate in amount and quality, and has been or can be made continuous use for man’s exploitation.
It has 3 attributes as following:
It is limited in amount.
It possesses both social attributes and natural attributes.
It is measured by quantity and quality standard.
The dualism of water resources determines the comprehensive characters of water resources system. It is a combination of both natural water and social water, as well as a mix of natural water resources, usable water resources, available water supply, and water demand and consumed by social economy, etc. Water resources system is also a complicated large system, which contains regional background, as well as specific framework, function and dynamic balance.
The evaluation of the water resources system requires the evaluation of water resources carrying capacity, and the supervision with the viewpoint of sustainable development. The term of water resources system carrying capacity has two meanings, one is water environment carrying capacity, and the other is water resources carrying capacity. The former, the carrying capacity of water environment refers to the ability carrying and containing pollutes and polluted water in certain water area, where the water resources is renewable and self-cleaning to be used continuously and maintain a good ecosystem. The latter, the carrying capacity of water resources refers to the ability supplying for the economic social development and maintaining a good ecosystem in certain drainage area or region. The carrying capacity of water environment and the carrying capacity of water resources are both depending on and restricting each other. And the co-relationship and matching of them determine the status of the function, structure and balance of water resources system.
2.2 Elements and relationship inside water resources system
The water resources system can be divided into two subsystems: the natural water subsystem and the social water subsystem.
For the natural water subsystem, the total water resources (including both surface and subsurface water) is made up of water resources in situ, passing by and diverted. While the ecological water requirement of natural system are supplied by natural water subsystem, the residual water are called usable water resources. There are great relationships between ecological water requirement and water environment carrying capacity, between usable water and water resources carrying capacity, as well as between water environment carrying capacity and water resources carrying capacity.
As to the social water subsystem, it is mainly social economical water requirement, using the available water supply from the usable water resources provided by natural subsystem. The social economic water requirement is including consumed water and surplus water. The surplus water has impact on water environment carrying capacity through Point-source, area-source and inner-source polluting [7]. Elements of water resources system and the relationship are shown in Figure 1.
For
example, the mean annual water resources in situ of
In the year of 2002, the test of diversion from the
Changjiang River
to
In 2002, from Jan 30th to Mar 31st, the total amount of water drawn from the Changjiang River to Changshu junction of the Wangyu River added up to 1.028×109 m3, whereas 6.47×108 m3 through Wanting junction into Lake Taihu, and 6.2×108 m3 through Taipu Gate to the lower reach of the drainage area, among which 3.8×108 m3 were supplied for Shanghai City.
In
2004, from Jan 1st to Dec 21st, the total amount of water
drawn from the Changjiang River to Changshu junction added up to 2.2×109 m3, whereas 1.012×109 m3 through Wanting
junction into Lake Taihu , and 1.429×109 m3 through
In
2005, from Jan 1st to Apr 30th, the total amount of water
drawn from the Changjiang River to Changshu junction of Wangyu
River added up to 1.32×108 m3, whereas 5.71×108 m3 through
In
2006, from Jan 1st to May 17th, the total amount of water
drawn from the Changjiang River to Changshu junction added up to 2.81×108 m3, whereas 7.56×108 m3 through
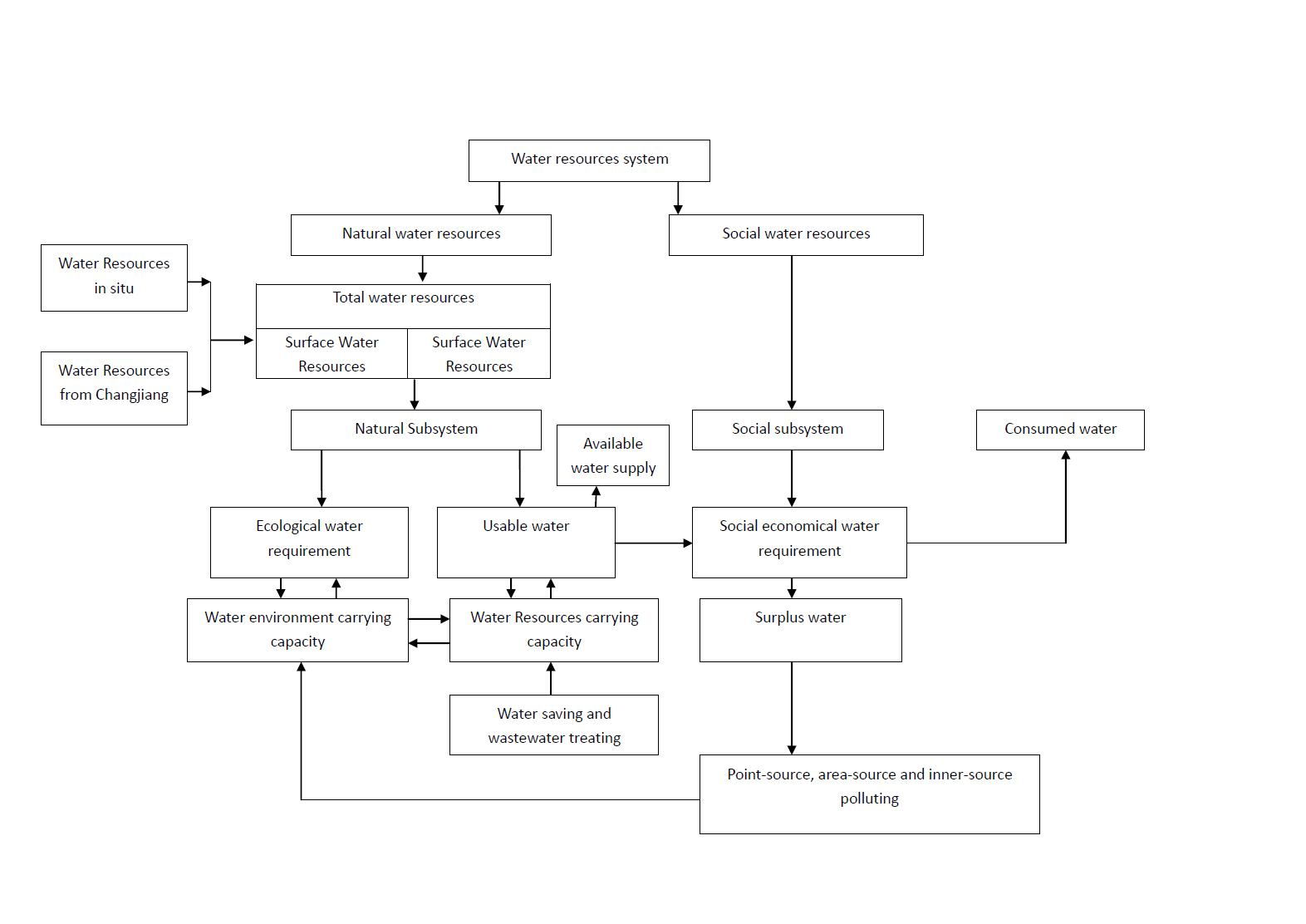
Figure 1 The
relationship between elements of water resources system of
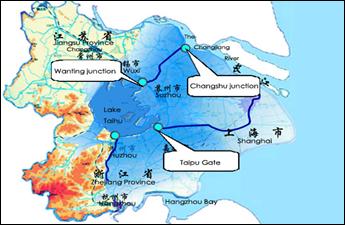
Figure 2 Sketch map of diversion from the Changjiang River to Taihu Lake
By such diversion in the recent years, the water supplied for drainage area is effectively increased, and the water environment is also greatly improved.
For example, during the period from Dec 17th
to 21st in the year of 2004, all kinds of water-quality index are
improved, main index like CODMn and TP of water supplied for Suzhou
from the Xitang River had met level Ⅱ~ Ⅲ. All these
enhance the carrying capacity of water resources system of
3 Degeneration of Water Resources System in
Lake Taihu
drainage area is one of most densely populated areas in
With
the rapid development of economic society, water resources system in
Water
quality of
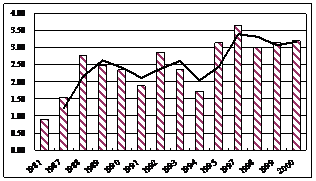
Figure 3
Variations over past 25 years of total nitrogen (TN) in the
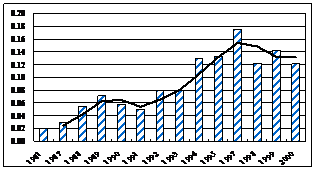
Figure 4
Variations over past 25 years of total phosphorus (TP) in the
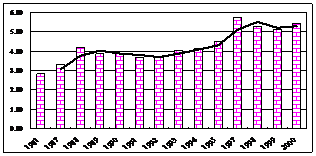
Figure 5 Variations over past 25 years of
chemical oxygen demand of Manganese (CODMn) in the
In general, water quality of
From 1950’s to 1970’s,
except for the Suzhou River, Huangpu
River and Jiangnan Channel, water
quality of other river channels in
Table 1
Water quality of river channels evaluated in
|
Year |
Length of river channels evaluated (km) |
Ⅰ ~ Ⅱ (%) |
Ⅲ (%) |
Ⅳ (%) |
Ⅴ ~ >Ⅴ (%) |
|
1987 |
1198.5 |
15.3 |
23.6 |
39.0 |
22.1 |
|
1988 |
1155.0 |
13.9 |
28.0 |
29.8 |
28.3 |
|
1989 |
1129.0 |
6.0 |
38.7 |
28.2 |
27.1 |
|
1990 |
1163.2 |
13.5 |
28.9 |
33.9 |
23.7 |
|
1991 |
1177.7 |
21.4 |
31.3 |
17.1 |
30.2 |
|
1992 |
1165.7 |
8.2 |
18.7 |
35.2 |
37.9 |
|
1993 |
1118.1 |
25.5 |
15.3 |
26.0 |
33.2 |
|
1994 |
1072.6 |
12.1 |
15.3 |
26.3 |
46.3 |
|
1995 |
977.0 |
4.1 |
17.2 |
28.5 |
50.2 |
|
1996 |
1239.7 |
- |
13.9 |
36.9 |
49.2 |
|
2000 |
1598.0 |
0.7 |
18.7 |
27.2 |
53.4 |
Data from [12].
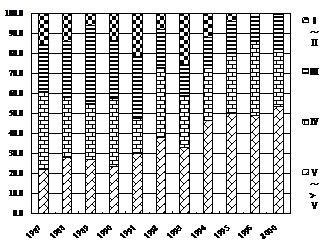
Figure 6 Water
quality of river channels evaluated in
4 Concept of Circular Economy
Circular economy is defined as the formation of the development of ecological economics, which follows the law of substance circle and energy flow of natural ecosystem and constructs economy system, making it bring into substance and energy circular utilization process of natural ecosystem. It is characterized by cleaner production, resources circular utilization and waste efficient recovery. The birth of circular economy develops the useful and discards the useless of traditional development patterns. It is the necessary result of the society progress. The essence of circular economy is to adjust production relations, and the target is to maintain sustainable development [13]-[15]. The difference between circular economy and traditional economy is shown in Table 2.
Circular economy has three operation principles: Reducing, Reusing and Recycling, also called 3R principles. They constitute the basic thought, but their significances are not the same. Only the Reducing principle has the first status. Circular economy first aims to avoid producing waste.
Table 2 the comparison between traditional economy and circular economy
|
Items |
Traditional economy |
Circular economy |
|
General description |
open linear economy based on uni-direction flow of matter ----shepherd economy |
Economic network of closed energy and material cycle |
|
Main characteristics |
Three dimensional split in economy, society and environment |
Three dimensional conformity in economy, society and environment |
|
Resources flowing mode |
Depletion of natural resources→Traditional industrial products and supplies→Waste Disposal |
Use of natural resources→Green industry products and supplies→Renewable resources |
|
The exploitation of resources |
Unrenewable resources,extensive management; High exploitation, low utilization; Focuse on short-term and single-functioned utilization |
recycling resources and scientific management; low exploitation, high utilization; focused on persistence and intensive management |
|
Waste emission |
high emissions of waste;unfriendly to environment |
Low even zero emission of waste;friendly to environment |
|
Type of industry |
Emphasis on employment (Second industry) |
Emphasis on Tertiary industry (or tertiarization of Second industry) |
|
Target pursued |
economic benefit (maximization of profit) |
Economic benefit, Environmental benefits and Sustainable development of society |
|
Economy growth mode |
Quantity-oriented material growth |
Quality-oriented services growth |
|
Environment administration mode |
Open looped governance of end |
looped entire process control, stage prevention |
|
Basic principle |
Traditional theory such as Political Economics、Welfare economics, etc. |
Ecosystems theory、Industrial Ecology theory, etc |
|
Index of estimation |
Non-green single economic indicators (GDP、GNP、National income、average consumption, etc.) |
green system of national accounts including green accounting and green audit (green GDP, etc.) |
|
Core of evaluation system |
Labor productivity |
Resources productivity |
The idea of circular economy is first germinate in 1960’s, when the environmental conservation movement is arisen. The American economist Kenneth Ewert Boulding has put forward the “spaceship theory” (The Economics of the Coming Spaceship Earth, 1966), which is considered to be a presentation of early circular economy theory. The emergence of circular economy has promoted research on resources and environment of 1970’s and widen the later study of sustainable development, as well as connect the circular economy to the ecosystem. In 1990’s, the study of intelligent economy had given the circular economy even more meaning in respect of high-tech industrialization and a learning type society.
Circular economy is a way to realize the harmony and balance between resources and environment, man and nature, and it is of great significance in realizing a new type of industrialization in our country.
5 Restoring and Improving the Water Resources
System of
Enhancing
the utility of resources is of great significance to fulfilling sustained using
of natural resources. Circulating economy can enhance the utility of natural
resources to the greatest extent, and save large amounts of resources to be
taken advantages of by later generations. At the same time, it can also reduce
the discharge of contaminants and alleviate environmental pressure. It is
believed that, to restore the degenerated water resources system of
5.1 Integrated management of water resources
Non-fluent administration management system
of water resources is the root of low effectiveness of water resources utility
and wastefulness, which greatly aggravated the water crisis of
5.2 Insisting on “3R Principle”, saving and using water scientifically
The key is how to save and use water scientifically.
First of all, to built up and strengthened the notion of saving water that country of water is terribly short of water and urgently needs to save water in the whole nation through school education, professional training and mass media.
Secondly, to encourage water-saving and clean production, to put the system of using water by ration into practice, to strengthen the management of water demanding, and to set up the base for the production system that is characterized by circular economy.
Thirdly, Exploit and utilize non-traditional water resources, such as rainwater using, seawater desalting, waster water recycling, flood water using, etc.
Fourthly, to adjust measures to local conditions, to lift water price moderately and to change gradually the condition that water price deviates from water value.
Fifthly, to advocate rational and clean consumption, and to incorporate the consumption process into the circular economy system.
In this way, the aim of “two taking-the-lead”
of
Acknowledgement
Pure-hearted thanks to the academician of Chinese Academy
of Science, Professor Wang Ying in Nanjing
University, and Professor Zhu
Yuansheng in
References
[1] Wang Y., Healy T., Chen W., Wang D. & Bishop A. (2004) Water resource capacity, regulation, and sustainable utilization of the Changjiang River Delta. J. Coastal Res. SI43, 75-88.
[2]
Liu C. & Chen Z. (2001)
Analysis on
[3]
Wang S. (2001) Resources Water
Conservation: Human Coexisting with Nature Harmoniously.
[4]
Sun J. (2005) Discussions on
water - saving society establishment in the Taihu basin.
[5]
She Z. (1997) The Water-Land
Resources And The Regional Development In Yangtze River
Delta. University of Sciences & Technology of
[6]
Huang X. (2000) Layout and
Improvement of Lake Taihu basin.
[7] Wang D., Shi Y., Wang L. (2003) On water resources system of the Changjiang River Delta. J. Nanjing Uni. (Natural Sci.), 39(6): 822-830.
[8]
Gao Y., Mao X., Xu W. (2006)
Analyaia of the influence on the Taihu
Lake and the aera around: diversion
from the Yangtze River to
[9] Qin B., Wu Q., Gao J., Fan C., Xu G., Chen W., Mao R. & Chen Y. (2002) Water environmental issues in Lake Taihu: problems, causes and management. J.Natural Resour. 17(2), 221-228.
[10]
Huang Y. (2003) Water Environment
and Pollution Control of
[11]
Yang G., Wang D. (2003)
Economic Development, Water Environment and Water Disaster of
[12]
Ye S., Zhu W., Lin Z. (2002)
Water resources and water environment of
[13]
Niu W. (2004). Circular
economy: an ideal mode gaining sustainable development. J.
[14]
Wu J. (2004) Diversion from the
Changjiang River
to Lake Taihu
being the base of develping circular economy system of
[15]
Feng Z. (2004) On circular
economy. Soft Sci.
[16]
Ye S. & Huang W. (2001)
Research on water saving of
[17]
Qian Z. & Zhang G. (2001)
The Integrated and Special Reports on Sustainable Development of
[18]
Wu H., Zhang Y. (2005) Making
efforts on a full operation of diverting water from Yangtze to




