Achievements
STATUS AND PROSPECT ON EXPLOITATION AND UTILIZATION OF SALINE GROUNDWATER IN HEBEI PLAIN, CHINA
Gao Hongqiang1, Bi Fuke1, Liu Zhigang2, Chen Zongyu3, Luo Guozhong1, Liu Lijun1
1.Hebei Institute of Geological Survey,Shijiazhuang 050081;
2.Hebei Bureau of Geology and Mineral Investigation,Shijiazhuang 050081;
3. Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology,CAGS,Shijiazhuang 050061
Abstract: Hebei Plain is a one of the water scarce region in
Key words: Hebei Plain, saline groundwater, utilization mode, prospect, measures
Water resources play an important role in the sustainable social and economic development.
For alleviating the water crisis and improving the ecological environment in Hebei Plain, especially in the saline water region, Exploitation and rational utilization of saline groundwater are the valid measure to solve the above water and environmental problems
1 The Characteristics of Saline Groundwater Distribution in Hebei Plain
Greoundwaters with different TDS are distributed in whole
The TDS for saline groundwaters ranges from
Table 1 The area of saline groundwaters in the Hebei Plain
City | Area of groundwater with different TDS(km2) | ||||
1~ | 2~ | 3~ | > | Total | |
420.7 | 190.7 |
|
| 611.4 | |
1726.0 | 801.2 | 420.8 | 1580.5 | 4528.5 | |
337.5 | 428.8 | 4.5 |
| 770.8 | |
3512.0 | 625.5 | 110.4 | 21.1 | 4269.0 | |
Xingtai | 3280.7 | 2409.9 | 716.4 | 139.1 | 6546.1 |
253.8 | 6.0 |
|
| 259.8 | |
Cangzhou | 4954.8 | 3207.8 | 2470.1 | 2834.1 | 13466.8 |
Langfang | 4239.6 | 296.4 | 65.1 | 0.1 | 4601.2 |
Hengshui | 3417.6 | 3620.2 | 724.6 | 106.5 | 7868.9 |
Total | 22142.7 | 11586.5 | 4511.9 | 4681.4 | 42922.5 |
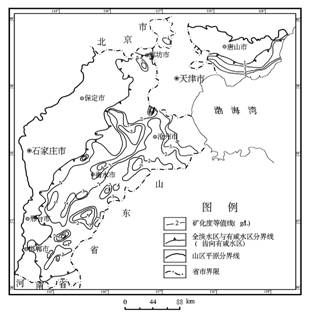
Fig.1 Distribution of saline groundwater in
The boundary of fresh and saline groundwater is approximately at front of distal fan (Figure 2) in the piedmont. The fresh groundwater is distributed in the piedmont in west part. And the saline groundwater is distributed in central and littoral plain in east part. The ship of saline water is approximately a cuneal water body that its thickness increases from west to east. The aquifer below this saline aquifer contains fresh water. Generally, the depth of upper boundary of saline aquifers ranges from
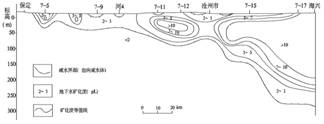
Fig. 2 TDS cross-section from
In summary, the characteristics of saline groundwater distribution are as follow:
(1)large distributed area. The area of saline groundwater is
(2)large water storage capacity. It is estimated that the storage capacity of saline groundwater is about 2111×
(3)shallow depth of water table. The depth of water table is 10~
(4)occurrence in different geologic formation. Both Holocene and Pleistocene formation may contain saline water.
(5)the upper boundary of saline aquifer is controlled by landform and the lower boundary is controlled by basal structure.
2 Exploitation and Utilization of Saline Groundwater
2.1 Present yield of saline groundwater
The brackish and saline groundwater has not been exploited in a lager scale in
Table 2 Yield of saline groundwater in 2003
City | Yield of different TDS( | ||||
1~ | 2~ | 3~ | > | Total | |
0.4428 | 0.1601 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6029 | |
1.8618 | 1.2395 | 0.5846 | 0.1462 | 3.8321 | |
0.9383 | 0.7977 | 0.0063 | 0.0000 | 1.7423 | |
4.0818 | 0.8398 | 0.0319 | 0.0291 | 4.9826 | |
Xingtai | 4.1109 | 3.0865 | 0.2972 | 0.1843 | 7.6789 |
0.5537 | 0.0106 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5643 | |
Canzhou | 4.6261 | 2.6581 | 0.9541 | 0.6800 | 8.9183 |
Langfang | 4.2762 | 0.1940 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 4.4702 |
Hengshui | 3.6590 | 3.7053 | 0.1898 | 0.0025 | 7.5566 |
Total | 24.5506 | 12.6916 | 2.0639 | 1.0421 | 40.3482 |
More than 90% exploiting saline groundwater was used for irrigation. Industrial uses with 1.8×104m3/day has been pumped in Cangzhou city for fertilizer production since the 2000 year.
2.2 Types of utilization
At present, the brackish water was directly used for irrigation.
In the littoral area, saline groundwater was mainly used for aquiculture, such as crab and prawn. In addition, saline groundwater (TDS 3.2
Indirect uses of saline groundwater involve in rotational irrigation and proportion irrigation of fresh and saline water. Rotational irrigation is a scheme for alternating use of fresh and saline groundwater based on the water quality, crop types and salt tolerance in different growth stage. Proportion irrigation of fresh and saline water is a scheme of proportional mixing fresh and saline water for irrigation. The fraction of fresh and saline water is determined by the following equation:
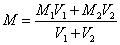
where: M-TDS of mixing water (g/L);
M1-TDS of saline water(g/L);
M2-TDS of s fresh water(g/L);
V1-volume of saline water(m3)
V2-volume of fresh water(m3)。
There are many areas using proportion irrigation for agriculture in
(1)Industrial use
A project for desalination of saline groundwater was finished and put into action in Cangzhou Chemical Corporation. Total 30 production wells with depth of 120
(2)Domestic uses
Desalted saline groundwater has been used for country water supply in Cangzhou. At present, there are hundreds of villages using desalted water.
The desalination method for Domestic uses is electro-dialysis. The saline water with TDS of 3
3 Importance of Exploitation and Utilization of Saline Groundwater
3.1 Increasing water resources
Saline groundwater is mainly distributed in the east part of
3.2 Enhancing water storage capacity
The shallow saline groundwater body occupied the space of the shallow aquifers and restricted the precipitation infiltration. Exploitation of shallow saline groundwater may decline the water table to an optimal depth and enhance water storage capacity of aquifer which lies 3
3.3 Improving eco-environment
Before 1980s, small amount of saline groundwater was exploited and used for irrigation. As the water table was very shallow, drought,flooding,Salinization and alkalization were occurred frequently. Thus, exploitation and utilization of saline groundwater is vital to mitigate these natural disasters.
After 1980s, more saline groundwater was exploited to meet the increasing demand for water. As a result, water table was declined and water loss by evaporation was reduced. Meanwhile, the Salinization was mitigated and the agricultural production was increased. In addition, the decline of water table disturbed natural flow regimes of saline groundwater. This is helpful for water infiltration, aquifer replenishment and increasing available resource.
3.4 Mitigating saline intrusion of fresh water aquifer
Owing to overexploitation of fresh groundwater from the deep confined aquifer, a hydraulic head difference occurred between saline water aquifer and fresh water aquifers. This induced the saline water leakage into the fresh water aquifer and caused salt contamination of fresh water. At the interface of saline and fresh water, the upper saline water intruded into lower confined aquifer. If it was possible to decline water table by exploitation of saline water, the hydraulic head difference between the two aquifers would be reduced. And then the risk of saline intrusion would be minimized.
4 Prospect on Exploitation and Utilization of Saline Groundwater
4.1 Potential of exploitation and utilization of saline groundwater
Since small amount of saline groundwater is exploited in the eastern plain, especially in littoral area, the saline groundwater is in the natural state. The water table is very shallow (2
Based on the data of water table in Dec. 2003, the areas for the depths of water table less than
Table 3 Available resources for the depths of water table less than
Depth of water table (m) | Average specific yield | No protected zone | Protected zone | ||||
Area (km2) | Thickness of aquifer (m) | Water resource ( | Area (km2) | Thickness of aquifer (m) | Water resource ( | ||
<2 | 0.075 | 635 | 9 | 4.3 | 0 | 9 | 0.0 |
2~4 | 0.06 | 6744 | 7 | 28.3 | 1874 | 7 | 7.9 |
4~7 | 0.06 | 12567 | 4.5 | 33.9 | 12567 | 4.5 | 33.9 |
7~10 | 0.065 | 12519 | 1.5 | 12.2 | 12519 | 1.5 | 12.2 |
total |
|
|
| 78.7 |
|
| 54.0 |
The average groundwater loss by evaporation in
4.2 Utilization for different purposes
(1)Irrigation
There are three types for irrigation by using saline groundwater, direct irrigation, rotational irrigation and proportion irrigation. Unlike irrigation by fresh water, saline water irrigation needs control the salinity for different crops because of salt tolerance. The salinity control requires the soil salt accumulation is less than salt tolerance. Rotational irrigation and proportion irrigation are the better way for controlling salinity.
(2)Industry
For the industry of low water quality requirement, such as chemical plant, power plant, textile mill, foundry and cement plant, the shallow saline groundwater may be used directly. For the large enterprises in littoral, deep saline groundwater (well depth >
(3)Drinking water for village
Desalination of saline water for drinking has been widely used in rural areas of
(4)Domestic uses for city
Dual water supply is a better way for city water supply system. In recent years, the dual water supply has been successfully tested in Cangzhou city by the water authority. Because the saline groundwater was not exploited a few years ago, precipitation could not infiltrate into aquifers and water table rise in spring season resulted in road frost boiling. In Oct.2002, a saline reclaimed water system was built in Cangzhou. After one year testing, the average monthly domestic water use for one person was
5 Suggestions and measures on exploitation and utilization of saline groundwaters
5.1 Hydrogeological investigation on saline groundwater
Before exploitation of saline groundwater, some information about aquifer property and water quality must be known. Thus, it is necessary to carry out hydrogeological investigation. In addition, some problems, such as land subsidence and sea water intrusion may occur due to water table decline after exploitation. It is also important to evaluate the environmental impact of groundwater development.
5.2 Consideration of local conditions, rational exploitation
Exploitation of saline groundwater should combine the concentrated and dispersed wells and focus on the shallow aquifer with well depth of 10
In addition, deep fresh groundwater in Tertiary aquifer is used by reinjection for oil production in Rinqiu and Jidong. It is necessary to study the reinjection of saline groundwater.
5.3 Promoting industrialization of desalination of saline water
Desalination of saline water is a new industrialization. Hebei Plain is a one of the water scarce region. However, there are plenty of brackish or saline groundwaters within the shallow aquifers. This provides a prerequisite and basis for desalination industrialization. The saline water desalting system with production of
5.4 Integrated water resources management and protection of geo-environment
In view of the status of water resources in Hebei province, on the principle of making overall plans and taking all factors into consideration, comprehensive development and rational utilization of water resources, combined use of surface water and groundwater, a long-term plan for exploiting saline groundwater should be made to prevent drought, waterlogging, salinity and saline. Groundwater monitoring is the basis of groundwater resource assessment and development. A saline groundwater monitoring network should be established as soon as possible in
A
5.5 Improving management work of government
In order to improve the technology for exploitation and utilization of saline groundwater, government should enhance the efficiency of resource utilization, encourage enterprises to use saline groundwater and provide financial support for the villages which use desalination of saline water as drinking water. At the same time, we must launch an extensive public awareness campaign on importance and prospect of using saline groundwater.
References
[1] Chen, W.H. 1999. Ground Water in
[2] Z.H., Zhang, Z.L. Shen, Y.Q. Xue, F.H. Ren, D.H. Shi, Z.Z.Yin, Z.X. Zhong, and X.H. Sun. 2000. Evolution of Ground Water Environment in the North China Plain.
[3] Li S.H., Huang W., Yan J.L., Zuo G.L. 2001. Make full advantage of salt water and saltish water resources and develop breed aquatics of high efficiently ecological patten.




