Achievements
THE GEOLOGIC CONDITION AND HYDRODYNAMIC MECHANISM OF SHUANGHE OILFIELD FORMATION
Fu Yong1,2,Wang Xiaofeng2,Wang Xiaodong2,Li Jianqi2
1.
2.
Abstract:Shuanghe oilfield,which has rich oil source and good reservoir and favorable trap and superior preservation, is of the geologic and hydrodynamic conditions to form big oilfield. It is in the low potential area of hydrodynamic action where the contour of water head is wide and sparse and fluid energy exchanges easily and energy equilibrium is strong. Meanwhile it comes between the east high value and west high value forming very good convergent flow. Therefore it is a very favorable hydrodynamic condition for forming Shuanghe Oilfield.
Key wards:geologic condition; hydrodynamic action;hydrocarbon accumulation;Shuanghe Oilfield
Groundwater dynamic condition is the key factor to control hydrocarbon, and secondary migration period, direction, history and favorable accumulative area[1]. As hydrocarbon carrier, groundwater movement has an influence on migration, accumulation and distribution of hydrocarbon in the basin[2]. Therefore, hydrodynamic research is one of the important ways for people to recognize hydrocarbon reservoir, to predict hydrocarbon distribution regulation, and to guide hydrocarbon exploration[3]. In the late 20th century, many scholars at home and abroad carried out a great amount of investigation on hydrodynamic mechanism of oilfield formation in hydrocarbon-bearing basin and set up a close relationship between hydrodynamics and hydrocarbon accumulation[4-11]. This paper discusses the problem of mechanism of hydrocarbon accumulation through the study on geologic condition and hydrodynamic mechanism in forming Shuanghe Oilfield in Biyang depression.
1 Regional Geologic Background
Shuanghe Oilfield, situated in the southwest part of Biyang depression, is a famous large oilfield with the oil output of one hundred million.Its geologic reserves occupy half of whole depression proved reserves.It is the largest oilfield inside the depression. Biyang depression is in the boundary of Tanghe and
2 The Geologic Condition of Shuanghe Oilfield Formation
2.1 Rich oil source condition
During Eh3 sediment period, Shuanghe district, located in shallow lake face, not only was next to oil source center but also had deposited very thick oil source rocks by itself. These oil source rocks have the characteristics of plentiful organic matter, good type of organic matter, high geothermal gradient (

Fig 1 The plane and section of updip pinching reservoir in Shuanghe Oilfield(from QIU Zhongjian,1999)
2.2 Good reservoirs
The sandstone bodies of Shuanghe delta, located at southern steep slope, inserted oil source area during the period of whole Eh3 deposition. They were deposited with oil source rocks alternately and were enclosed by oil source rocks completely and located in the direction area of hydrocarbon migration and formed a good structural combination of source and reservoir and cap.
2.3 Favorable trap condition
It is well known that although lake face deposit is downdip pinching under virgin state.But Shuanghe Oilfield forms updip pinching because of special structure of Biyang depression. The lake boundary which enlarged continuously during Eh3 period formed a series of pinching sand bodies towards the northwestward (fig 1). After the deposition of Eh3, The water in the lake begun to wither, northern part of the depression lifted up gradually, south subsidence was affected by the big boundary fracture, and the subsiding center migrated southward step by step. At the end of Neogene period, the subsiding center had migrated to Anpeng District near the big boundary fracture, which induced the northwest of Shuanghe sand body lifted up partly from normal downdip pinching to updip pinching. These sandstones pinching lines intersect vertically with structural contour, forming large area hydrocarbon reservoir of lithologic trap.
2.4 Favorable preservation condition
Shuanghe Oilfield develops a set of 100—
3 Hydrodynamics of Shuanghe Oilfield Formation
The forming condition of Shuanghe Oilfield have been studied a lot[13,15-18], but seldom studied from the angle of hydrodynamics. The origin of Shuanghe Oilfield will be discussed in the followings.
Hydrodynamics has a close relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation. Wang Jie et al[19] think that the bigger the gradient in the close zone of water head contour, the stronger join forces(buoyancy and hydrodynamic) acting on the oil. But it indicates simultaneously that fluid energy exchanges difficultly in the direction. The sparseness position of contour indicates that fluid energy exchanges easily, the equilibrium action of its energy must be strong, low potential zone in the direction is the main direction of oil migration, the difference of flow energy exchange which was induced by the dissimilarity of potential gradient must result in the change of the migration of oil and gas, the result is that it can be collected in low potential zone which has little change of potential gradient. It shows in figure 2, Shuanghe oilfield belongs to low potential zone of hydrodynamics, the water head contours of Eh3 and Eh2 are rather wide, slow and sparse, flow energy can change easily, the equilibrium action of the energy is strong, succession of hydrodynamics is obvious, and it is next to high value zone of water head of depression center, forming the main direction of migration of oil and gas. On the one hand, according to LIU Guangdi’ study[20], flow together is of favorable to hydrocarbon accumulation. We can see from figure 2 that the western part of Shuanghe Oilfield (near B27) is one subaltern high value zone of water head, which make the oilfield locate between eastern and western high values, forming very good convergent flow , which creates the most favorable Hydrodynamics to form Shuanghe Oilfield, on the other hand, based on CHEN Fajing and TIAN Shicheng’ study[21], the main period of the migration of oil and gas in Biyang depression is during the end period of El after forming updip pinching on the sandstone in Shuanghe Oilfield, which provides trap condition for hydrocarbon migration. Because of the same direction for hydrodynamics and buoyancy, the hydrocarbon from oil source center can inject continuously under the influence of hydrodynamics and buoyancy, filling oil with each layer in Shuanghe oilfield.
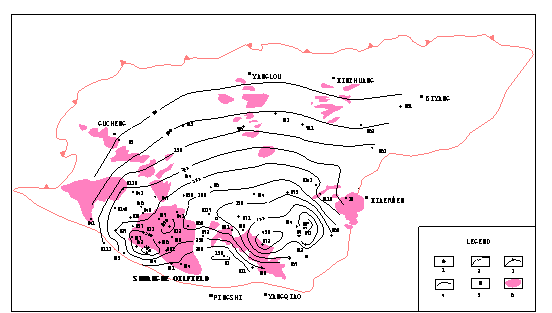
Fig 2 Eh3 hydrodynamic map in Biyang depression
1 well; 2 contour of sedimentary water; 3 pinching line; 4 boundary line; 5 placename; 6 oilfield
4 Conclusion
Hydrodynamics is important to form Shuanghe Oilfield. Hydrodynamic field in the whole Biyang depression forms very good flow together near Shuanghe Oilfield, water head contour is rather wide, slow and sparse, adding unique trap condition of updip pinching of sandstone, which creates the most favorable Hydrodynamics to form Shuanghe Oilfield.
Reference
[1] Chen Heli.The efficiency way to research migration of hydrocarbon.Oil and gas geology, 1995,16(2):126-131.
[2] Yang Xuchong.On the underground hydrodynamic environment in an oil and gas basin.Acta Petrolei Sinica,1989,10(4):27-34.
[3] Lou Zhanghua,Jin Aimin and Tian Weizhuo.Origin and evolution of hydrodynamics and the migration,accumulation of petroleum in continental petroliferous sedimentary basins.Chinese journal of geology,2005,40(3):305-318.
[4] Hitchon B.Geothermal gradients,hydrodynamics,and hydrocarbon occur rences,Alberta,Canada[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1984,68(b):713~743.
[5] Gosnold W D.Heat flow and groundwater flow in the Great Plains of th e United States[J]. Journal of Geodynamics,1985,4:247~264.
[6] Garven G.A hydrogeologic model for the formation of the giant oil sa nds deposits of Western Canada Sedimentary Basin[J]. American Journal of Science,1989,289:105~166.
[7] Person M,Garven C.Hydrologic constraints on Petroleum generation within continental rift basins: Theory and application to the Rhine Graben[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1992,76(4) :468~488.
[8] Bachu S,Underschultz J R.Hydrogeology of formation waters,Northeastern Alberta Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin,1993,77(10):1745~1768.
[9] Wang Zhixin,Xin Quanlin.The feature of hydrodynamics of press water in Dongying depression. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1998,19(4):21-25.
[10] Zeng Jianhui.Hydrodynamic characteristics and its effect on oil-gas migration and accumulation in Taibei depression.Acta sedimentologica sinica,2000,18(2):273-278.
[11] Kang Zhihong,Kang Yangfang,Deng Lin.Application of palaeohydrodynamic modeling to Tarim basin.Oil and gas geology.2001,22(3):270-272.
[12] Luo Jiaqun.Reservoiring patterns of oil and gas in the deep layer of Biyang depression. Oil and gas geology.2003,24(1):55-57.
[13] Qin Weijun.Reservoiring factors of large structural-lithologic composite oil reservoir in Biyang depression. Oil and gas geology.2004,25(4):433-436.
[14] Qiu Zhongjian,Gong Zaisheng.China petroleum exploration.Beijing:Petroleum industry publishing house.1999.
[15] Zhu Shuian,Li Chunju,Chen Yongzheng.The depositional characteristics of underwater fan in Shuanghe,Biyang depression. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1983,4(1):11-16.
[16] Xu Shiyong,Yang Chunlin,Zhu Shaobi.The forming condition and accumulation of hydrocarbon in Biyang depression[A].The accumulation and distribution of hydrocarbon in China[C].
[17] Wang Shouqing,Xu Shiyong,Sun Xiubin.Shuanghe oilfield[A].China big oilfield of land face[C].
[18] Yin Wei,Wu Shenghe,Lin Sheqing.Study on mechanism of oil and gas accumulation in Shuanghe oilfield. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2003,24(5):40-45.
[19] Wang Jie,Guan Defan.Study on model of formation and migration and accumulation of hydrocarbon.
[20] Liu Guangdi.Analysis to accumulation units of hydrocarbon. Chinese journal of geology, 2003,38(3):307-314.
[21] Chen Fajing,Tian Shicheng.Compaction and migration of hydrocarbon.Wuhan:publishing house of geology




