Achievements
THE IRREVERSIBLE PROCESS IN GROUNDWATER SYSTEM
Feng Quanzhou Wangping Yue Chaojun
(
Abstract: By reviewing the evolving history of the groundwater system in a city area, it is discovered that the advent of a new system structure is achieved through the process of mutation, and the whole process is irreversible; it is further believed that, under the influence of continuous artificial exploitation, the groundwater system makes necessary structural adjustments to meet the demands imposed on the performance of the whole system; furthermore, through evolvement, the whole system degenerates into a thermo-dynamic system, leading to the increase of its entropy. The general model for the evolvement of groundwater system goes as such: natural structure-evolving structure- degenerative structure.
Key wards: the evolvement of groundwater system, irreversible process, system structure, model of evolvement
1 Introduction
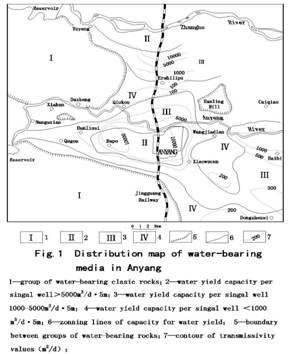
Generally speaking, geology is , from the
perspective of evolvement, mainly concerned with the composition and
development of the earth; however, hydrogeology, as an important branch of
geology, rarely takes into account the key concept of “evolvement”, so the
evolvement and degeneration of system structures are often overlooked during
the function simulation and state prediction for groundwater. In light of the
groundwater hydrograph , in connection with factors such as the evolving
history of inter replenish and discharge between groundwater and surface water,
and the flowing field evolvement of groundwater in all phases, the evolvement
history of a groundwater system is reproduced, and some discussions are carried
out about the irreversible process of groundwater system. In Anyang, a medium
sized city situated in the northern part of Henan Province, due to the ever
increasing rate of groundwater exploitation, the relationship between
extraction and replenishment for groundwater system experienced the following
three phases: natural
adjustment phase, rechargeable drainage phase and over-exploitation phase. At the result, the groundwater resources is in red deficit, and the groundwater ,as well as surface water, which containing different kinds of dissolved agents, converged towards the concentrating extraction areas, leading to the degeneration of geo-environment quality. The above phenomenon are pervasive in those cities in Northern China.
With an total area amounting to 1000km , part of the study
area falls within
2 The Evolution History of Ground- water Flow system
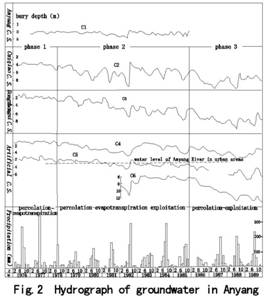
In light of the hydrograph of ground water, it is noticeable that, due to the ever increasing artificial exploitation, the groundwater system has experienced three dynamic response phases (Fig.2). the first phase started well before June,1978;the second stage started in June 1978,and lasted until the end of 1985; the third phase has started well after 1986.The procedure of the three phases produces abundant insight into the characters of the groundwater system..
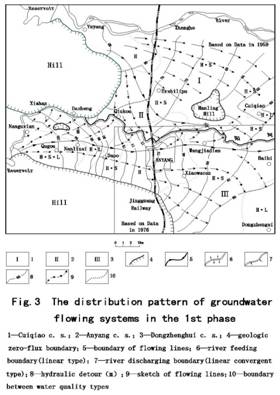
During the first phase, because the groundwater exploitation was slight, the groundwater system maintained a natural balance between recharge and discharge. The framework of groundwater system consisted of three natural sink systems (Cuiqiao sink system, An Yang sink system and Dongzhengsi sink system), which were located in order from N to S in the study area (Fig.3) . In Cuiqiao sink system , groundwater flowed towards Cuiqiao, the southern border of flow lines was located to the south of Hanling; Within An Yang sink system, the east running section of Anyang River absorbed flow lines, hence it discharged groundwater, in the region between the two borders for flow lines, which were situated in the north and south of the region separately, the western part was the linear recharge border from river, thus the groundwater system was recharged by Anyang River; Dongzhengsi sink system was situated in the south(Ⅲ), in which groundwater flowed eastwards and converged towards Dongzhengsi.
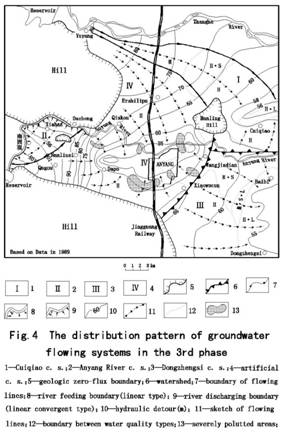
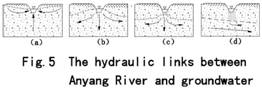
During the 3rd phase (1986-1990), due to intensive
artificial discharge, the groundwater resources was over exploited, so this
phase is characterized with an artificial sink. In the groundwater system ,
except one artificial sink system caused by artificial intensive exploitation,
the rest three sink systems are all the remnants of natural ones (Fig.4). In
comparison to the first phase, Cuiqiao sink system(Ⅰ) shrunk greatly, the southern flow lines border was
pushed up northwards for about 7.0km;Anyang
sink system(Ⅱ) shrunk westwards greatly also, with the remaining
part situated at the corner of Anyang River. The Dongzhengsi sink system (Ⅲ) , which is situated to the SE of Anyang City, was
the result of artificial capture during the 1st phase, and was
bordered with the artificial sink system by divide; in the middle part of the
region was the artificial sink system(Ⅳ),in which groundwater flowed towards the center of
the cone of depression. At this phase, four kinds of recharge –discharge
relationships coexisted (Fig.5): in the Anyang River sink system (Ⅱ), there was a unity of potentials field and a close
hydraulic linkage between groundwater and river (Fig.5,b), i.e. in the east
section of Anyang River it discharged groundwater(note that , although there
are vertical flowing vectors in both horizontal-recharge and horizontal-
discharge, the word “horizontal” is used here as ever ,Fig.5,a), while in the north part, it replenished
groundwater; the up-conning of groundwater beneath Anyang River
made up the water divide between Cuiqiao sink
system and Dongzhengsi sink system, the two systems received the free
percolation recharge from
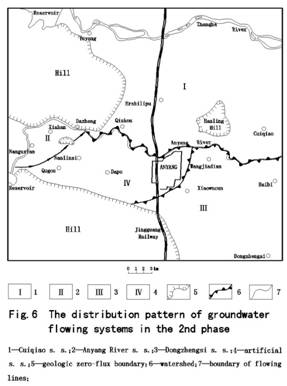
The 2nd phase (June 1978-end of 1985):In light of the general pattern of groundwater system in the 1st and 3rd phase , and taking into account the groundwater hydrograph curves, we can make some predictions on the evolvement of groundwater system in the 2nd phase(Fig.6) : the 2nd phase is the transitional phase between 1st and 3rd phase ; in the section to the east of Anyanghe bridge , where it had discharged groundwater during the first phase, Anyang River replenished groundwater; Anyang River constituted into the divide for groundwater, the framework of the groundwater system include: artificial sink system(Ⅵ),Dongzhengsi sink system(Ⅲ),Anyang River sink system(Ⅱ)and Cuiqiao sink system(Ⅰ).
3 Some Discussions about Irreversible Process in Groundwater System
During the evolution process from phase 1 to phase3, the groundwater balance and regime, the hydraulic links between groundwater and surface water, the constituents of groundwater resources, the groundwater flowing field and chemical field, all underwent deep changes;these changes were achieved through ups and downs in the structure of groundwater system in the process of realizing its water supply purpose. When the abnormal ups and downs break through a critical point, a catastrophic shift occurs, resulting in the formation of a new structure, hens the evolution of the system embarks on a new procedure. Here, we refer to the system structure, which can not only meet the water supply demand , but also don not inflict too heavy burden on environment , as an evolving structure; however, we terms a structure ,which can only (or can not either)meet water supply demand at the expense of environment ,as a degenerative structure. Under the influence of continuous artificial exploitation, the evolution sequence of groundwater system structure goes like this: natural structure-degenerative structure, and the evolution process is irreversible.
3.1 The natural structure of groundwater system
During the
first phase, thanks to the slight exploitation, the groundwater system
maintained a natural balance between recharge and discharge. Groundwater mainly
received recharges from precipitation and horizontal percolation from
The spatial orderliness of a system result in its stability over time (fig.2, phase 1).The uneventful curves of groundwater hydrograph observed in the five monitoring boreholes show that the above sink systems were closely interrelated. As a whole, it exhibits high stability; the fact that its yearly fluctuation was around 1m, the peak of hydrograph curves seemed similar to smooth hillock tops, indicate that the system had strong wave filtering function., the effects of rainfalls are offset by evaporation and discharge through river, and the transmission of potential energy between sink systems.
An
interesting chemical field of ground water is also derived from the spatial
orderliness and steadiness, the aqueous chemical features ,which are dominant
in the region, formed in the phase .In the area situated to the east of Anyang
City , from source to convergence, which is constituted by parts of Cuiqiao and
Dongzhengsi sink systems, the transitional series of chemical composition types
is H_H.S_H.L, water quality in resource area is usually good, while saline
water occurs in the sink points which are accompanied by large patches of saline-alkali
land; the general pattern of groundwater flow shows that the chemical tracing
flow lines tended to be more mature towards the sink points, where all kinds of
dissolved agents built up. In the western part of Dongzhengsi sink system
,which was situated to the west of Anyang City, in the course of flow, the
transitional series of chemical composition types is H.S.L—H.L—H.S—H ,in the
course of flow. The explanation for the above phenomenon goes like this: as
aquifers became thinner in the vicinity of Nanliusi
Village, water flow became less fluent
owing to cementation of aquifers, leading to the midway building up of
dissolved agents and the occurrence of water composition types in the range of
H.S.L -H.L between Qugou Village and
3.2 The evolution of system structure
In the period
between June 1978 and 1985, the system deviated from the normal scope of ups
and downs, resulting in abnormal ups and downs, thus, the macro-steady state
was broken up(Fig.2,the curve in 2nd phase),till another
macro-steady state was produced through the self organizing mechanism in the
2nd phase(Fig.2,the curve in 2nd phase ). Though the groundwater
level kept lowering, it was still above the Anyang River(fig.2), hence the
system remained to be a natural one; owning to the increase of the exploitation
of groundwater in urban area for industrial purposes, the level of groundwater
had been lowered below Anyang River by 1981, attributing to the formation of a
new system structure by mutation; the eastern part of Anyang River beyond
Dazheng Village, where the river had discharged groundwater, turned out to be a
divide of groundwater, making up a replenishment boundary for groundwater;
Anyang River sink system retreated westward till the vicinity of Xiahan
Village(fig.4); Cuiqiaohui sink system was situated to the north of Anyang
River(Ⅰ),what lied to the south of Anyang river ,including
urban area and the area beyond the west of urban area ,was an artificial sink
system. The original Dongzhengsi sink system(Ⅲ)(fig.2)was cut off by Anyang River, resulting in the
formation of a divide of groundwater in the eastern part of urban area.,
leaving the remaining of Dongzhengsi sink system at the east side of the
divide. Realization of function led to the evolution of system structure, and
the evolved structure could maximize its capture from
In the period
from July 1982 through 1985,under the influence of the new structure, a new
feedback relationship was set up between the artificial exploitation, side
percolation from Anyang River, and replenishment by precipitation, attributing
to the relative stability of the system state (fig.2,the curves of boreholes C4,C5 in the second phase). There was a wave bottom of long endurance in C4,
which was far off the urban area; meanwhile, there was only a relatively stable
platform period inC5. The above phenomena can be explained as such: due to the
great amount of exploitation for industrial purposes in the urban area , long
lasting wave crests of groundwater hydrograph were inhibited, and the
uneventful replenishment from
3.3 The emergence of degenerative structure
During the period from 1986 to 1990, with the increasing rate of exploitation for industrial purpose, the evolved structure could no longer meet the demands of its function, at the center of the cone of depression, underground water table dropped almost vertically(fig.2,hydrograph curve of C6 in 2nd phase),and in the mean time, the whole water system experienced two big events, made the system evolvement reach its critical point, leading to the cropping –up of degenerative structure.
When the
underground water level dropped down near the critical position, the feeding
model via Anyang river changed from side-feeding
to vertical feeding in the east running section of
Because the
degenerative structure couldn’t generate any new feeding, the dropping-down of
underground water level at the center of cone of depression became dramatic. At
the west end of the region, due to over extraction of cobble and gravel
aquifers, the drawdown caused by extraction neared to half of the thickness of
phreatic aquifer until June 1990 ;at the same time, due to the descending of
water table in large areas , large numbers of suspending pumps appeared in
wells for agricultural irrigation. Because the artificial sink systems had no
natural outlets ,all kinds of dissolved agents gathered up near the center of
cone of depression, the groundwater quality was in grave state. The groundwater
of H.S type has migrated to the center of the cone of depression, and replaced
the original H –water there,and the high hardness water would follow up; several
heavily polluted groundwater bodies around the cone of depression kept on
flowing towards the center of urban areas. When
4 Conclusions
A groundwater system is characterized by self –organizing criticality .Around the critical point, the ups and downs of the system often touches off new structure. Under the influence of ever increasing artificial exploitation the definite evolvement model for a groundwater system is natural structure-evolving structure- degenerative structure, and the process is irreversible. The evolvement from natural structure to evolved structure is a process in which the system absorb negative entropy influx in order to achieve its function for water supply. When the groundwater level drops to a critical point, a catastrophic shift occurs, and a new orderly structure appears; the newly formed structure is able to generate recharge from rivers and capture run-offs and evaporation from neighboring regions, and the system evolves towards the decrease of entropy to better meet the requirements by its function. When groundwater level keeps dropping down, and the system cannot meet the requirement for water supply, a resultant change in the state of system follow up definitely. When the groundwater level drops to another critical point, the above changes of state will bring about massive ups and downs, leading to the catastrophic shift in its structure; the relationship between replenishment and discharge is broken up, resulting in the formation of a degenerative structure; however, the degenerative structure can not generate new negative influx, the system can only evolve towards the increasing of its entropy.
Some thoughts in this paper were inspired by Professor Zhang Renquan and Proferssor Xu Hengli during my study in China University of Geosciences. I sincerely acknowledge them for their valuable guidance.
参考文献
[1] 王大纯 张人权等 水文地质学基础[M] 北京 地质出板社 1995年6月
[2] 徐恒力 张人权等 地下水系统分析[M] 北京 地质出板社 1995年6月
[3] 宋 毅 何国祥 耗散结构论[M] 北京 中国展望出板社 1986年10月
[4] 冯全洲 地下水流动系统的宏观识别及划分方案[J] 工程勘察 1993 121(2)



